Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Description
The mouse/rat angiopoietin-like protein 3 ELISA is to be used for the in vitro quantitative determination of mouse or rat angiopoietin-like protein 3 (ANGPTL3) in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatant. This ELISA Kit is for research use only.
Applications
Serum, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
100 ul/well
Shipping
On blue ice packs. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
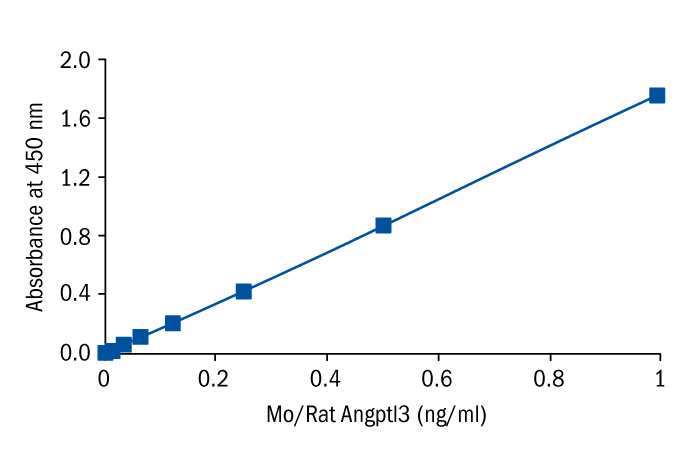
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.016–1 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
15 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 4,5%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 6.4%
Spiking Recovery
100%
Dilution Linearity
91-106%
Specificity
This ELISA is specific for the measurement of natural and recombinant mouse or rat ANGPTL3. It does not cross-react mouse ANGPTL4, mouse adiponectin, mouse resistin, mouse RBP4, mouse vaspin, mouse Nampt, mouse clusterin, mouse GPX3, mouse progranulin, mouse IL-33, mouse leptin, mouse RELM-β, human ANGPTL3, human ANGPTL4, human Nampt, rat Nampt.
Features
- RUO
- calibration range 0.016-1 ng/ml
- limit of detection 15 pg/ml
Research topic
Energy metabolism and body weight regulation, Oncology, Animal studies
Summary
The angiopoietins are a family of growth factors that are specific for vascular endothelium. Conklin et al. (1) isolated a full-length cDNA encoding angiopoietin-like protein 3 (ANGPTL3) from a human fetal liver/spleen cDNA library. The deduced 460-amino acid ANGPTL3 protein has the characteristic structure of angiopoietins: a signal peptide, an extended helical domain predicted to form dimeric or trimeric coiled-coils, a short linker peptide, and a globular fibrinogen-like domain (FLD). Human ANGPTL3 shares 76% amino acid sequence identity with mouse Angptl3. Northern blot analysis of human tissues showed a preferential expression of 4 ANGPTL3 transcripts being 4.5, 3.0, 2.8, and 1.7 kb in liver. Camenisch et al. (2) determined showed that ANGPTL3 induced angiogenesis in the rat corneal assay. The FLD alone was sufficient to induce endothelial cell adhesion and in vivo angiogenesis. By microarray analysis, Zhang et al. (3) showed that mouse hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)-supportive fetal liver CD3-positive cells expressed Angptl2 and Angptl3. Long-term HSC expansion occurred when HSCs were cultured in the presence of Angptl2 and Angptl3 together with saturating levels of other growth factors, concluding that angiopoietin-like proteins can be potent stimulators of ex vivo expansion of HSCs. The KK obese mouse is moderately obese and has abnormally high levels of plasma insulin, glucose, and lipids. Koishi et al. (4) observed a mutant mouse strain named KK/San, which showed a hypolipidemia. By positional cloning, they discovered a genetic locus encoding a unique angiopoietin-like lipoprotein modulator was responsible for such hypolipidemia. It was found to be identical to angiopoietin-like protein-3, encoded by Angptl3, and had a highly conserved counterpart in humans. Overexpression of Angptl3 or intravenous injection of the purified protein in KK/San mice elicited an increase in circulating plasma lipid levels. These data suggested that Angptl3 regulates lipid metabolism in animals. The authors suggested the possibility that genetic variation in ANGPTL3 contributes to atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus.
In vitro analysis of recombinant protein revealed that Angptl3 directly inhibits both endothelial lipase and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity (5, 6). Another line of evidence suggests that ANGPTL3 play an important role in regulation of HDL synthesis (7). The implication of ANGPTL3 in a number of metabolic dysfunctions suggests that ANGPTL3 is a novel predictor of these.
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Find documents for the lot