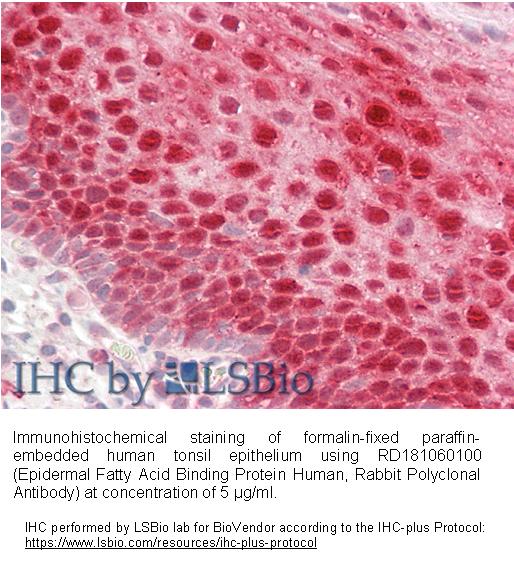
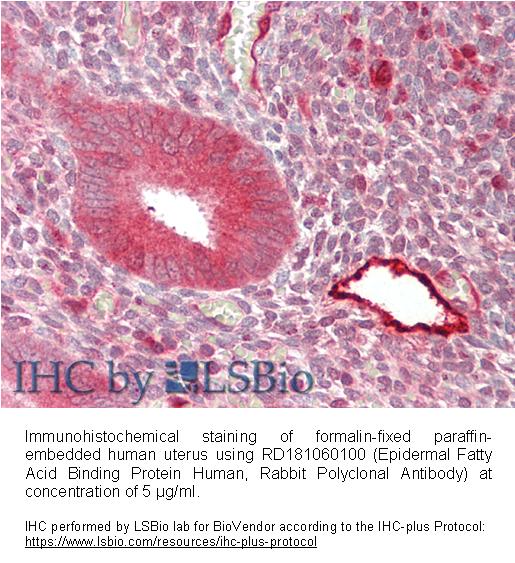
Type
Polyclonal Antibody
Applications
Western blotting, ELISA, Immunohistochemistry
Antibodies Applications
Source of Antigen
E. coli
Hosts
Rabbit
Preparation
The antibody was raised in rabbits by immunization with the recombinant Human FABP5.
Amino Acid Sequence
The immunization antigen (15.2 kDa) is a protein containing 135 AA of recombinant Human FABP5 and one extra AA, N-terminal methionin.
MATVQQLEGRWRLVDSKGFDEYMKELGVGIALRKMGAMAKPDCIITCDGKNLTIKTESTLKTTQFSCTLGEKFEETTADGRKTQTVCNFTDGALVQHQEWDGKESTITRKLKDGKLVVECVMNNVTCTRIYEKVE
Species Reactivity
Human. Not yet tested in other species.
Purification Method
Immunoaffinity chromatography on a column with immobilized recombinant Human FABP5.
Antibody Content
0.1 mg (determined by BCA method, BSA was used as a standard)
Formulation
The antibody is lyophilized in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.2.
Reconstitution
Add 0.2 ml of deionized water and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. Slight turbidity may occur after reconstitution, which does not affect activity of the antibody. In this case clarify the solution by centrifugation.
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
The lyophilized antibody remains stable and fully active until the expiry date when stored at -20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid repeated freezing/thawing cycles and store frozen at -80°C. Reconstituted antibody can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show decline in activity after one week at 4°C.
Quality Control Test
Indirect ELISA – to determine titer of the antibody SDS PAGE – to determine purity of the antibody BCA - to determine quantity of the antibody