Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
20 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
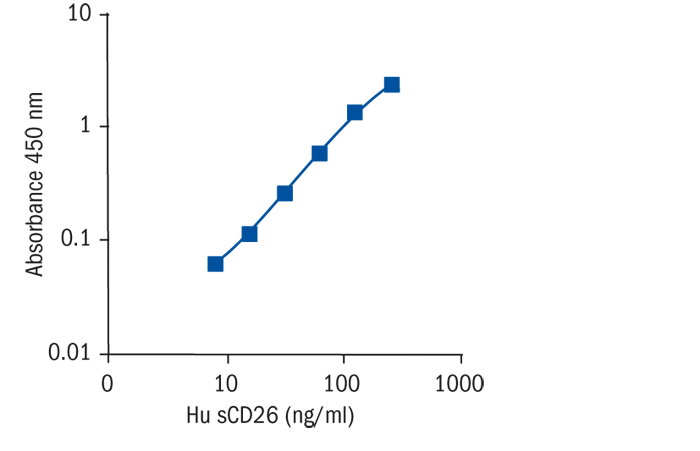
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
15.6–500 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
7.3 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 4.6%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 9.1%
Spiking Recovery
101,00%
Dilution Linearity
95,00%
Research topic
Cell surface proteins (sCD), Diabetology - Other Relevant Products
Summary
CD26, a T cell activation antigen, is a 110kDa cell surface glycoprotein with known dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV; EC 3.4.14.5) activity in its extracellular domain which is present on various cell types, including T cells and epithelial cells of the liver, kidney, and intestine.
Of the T cell antigens described to date, CD26 has proved to be one of the most intriguing in the scope of its functional associations. Considerable evidence suggests that CD26 can deliver a potent costimulatory signal to T-cells. This signal transducing property appears to be a property of its extracellular domain. In addition, CD26 appears to be a functional collagen receptor that may aid activated T-cells in localizing to inflammatory regions. It has also been demonstrated that CD26 not only acts as a functional dipeptidyl peptidase IV, but also binds strongly to adenosine deaminase.
Significant levels of DPPIV activity have been shown to exist in plasma, serum, and urine. The serum form of DPPIV is unique, and is not a breakdown product of membrane CD26, nevertheless exposing significant structural similarity to the membrane form.
Like many other T-cell molecules, CD26 is associated with HIV disease progression. There is a correlation of CD26 expression and HIV entry, replication and cytopathicity. CD26 has been identified as a key marker for monocytotropic HIV-1 infection, with a mechanism of early loss of CD26 - expressing cells in HIV-1 infected individuals described.
CD26 as an indicator of T-cell activation has been shown to fluctuate in parallel with several autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune thyroiditis. CD26 has been described as a marker that correlates well with the level of activity of these diseases. It has furthermore been studied as an indicator of the clinical progression in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis.
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Find documents for the lot