Type
Competitive ELISA, Immobilized antigen
Description
For the quantitative measurement of Triiodothyronine (T3) in human serum by an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay). Results shall be used in combination with other clinical and laboratory data to aid in the diagnosis of thyroid diseases in the general population.
This kit is intended for professional use only and is for laboratory use only. For research use only.
Applications
Serum
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Shipping
On blue ice packs. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
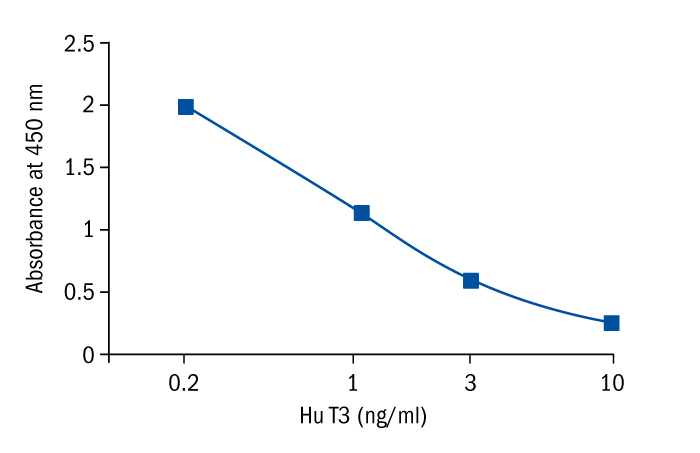
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.3–10 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.153 ng/ml
Features
- RUO
- calibration range 0.3-10 ng/ml
- limit of detection 0.153 ng/ml
- quality controls
Research topic
Others
Summary
Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are the two active thyroid hormones found in the blood stream. About 80% of T3 is produced by the deiodination of T4 in the peripheral tissue and the other 20% is produced directly from the thyroid gland. T3 is transported through the peripheral blood stream bound to serum proteins, namely thyroxine binding globulin, thyroid binding prealbumin and albumin. About 0.3% of the total T3 is unbound and is therefore considered the free fraction. T3 has an influence on oxygen consumption and heat production in virtually all tissues. The hormone also plays a critical role in growth, development, and sexual maturation of growing organisms.
T3 is one parameter used in the clinical diagnosis and differentiation of thyroid disease, particularly hyperthyroidism. In most hyperthyroid patients, both serum T3 and serum T4 levels are elevated. Serum T3 levels are a sensitive indicator of the impending hyperthyroid state often preceding elevated T4 and free thyroxine index values. Serum T3 levels are clinically significant in both the diagnosis of thyroid disease and in the detection of T3-thyrotoxicosis. However, it has been demonstrated that T3 levels may be affected by a number of medications, acute and chronic stress, and a variety of acute and chronic non-thyroidal illnesses. It is therefore necessary to differentiate those results that are due to thyroid dysfunction from those related to non-thyroidal diseases.
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Find documents for the lot