Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Urine, Amniotic fluid, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
20 µl (1:60 prediluted)
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
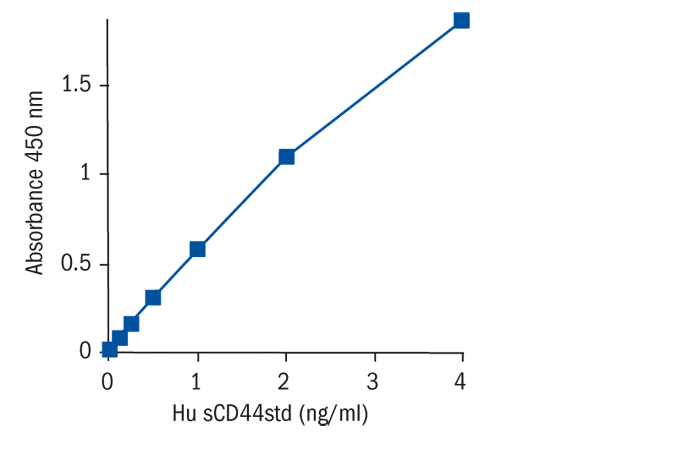
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.12–4 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.015 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 4.8%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 4.1%
Spiking Recovery
89,00%
Dilution Linearity
94,00%
Research topic
Cell adhesion proteins, Cell surface proteins (sCD), Extracellular matrix, Oncology
Summary
CD44 (85-250 kDa) is a polymorphic glycoprotein.
Determination of sCD44std will provide more detailed insight into different pathological modifications during cancer and other diseases.
- brain tumors: CD44 is strongly expressed in high-grade gliomas and weakly expressed in meningiomas, medulloblastomas and normal brain.
- colorectal carcinomas: in human colorectal neoplasia CD44 variant proteins are found on all invasive carcinomas and during carcinoma metastasis. Variants are already expressed at a relatively early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis and tumor progression.
- gastric cancer: tumors from patients suffering from stomach adenocarcinomas express CD44 variants. Adenocarcinomas of the intestinal type are strongly positive for exon v5 and v6, whereas diffuse type adenocarcinomas predominantly express exon v5.
- lung, breast cancer: in malignant tissues there is gross overproduction of alternatively-spliced large molecular variants in all samples, whereas in the control samples only the standard product was routinely detected with occasional minimal quantities of one or two small variants.
- lymphoma: in gastrointestinal lymphoma overexpression of CD44 has been correlated with poor survival and more disseminated disease (6,3). Overexpression of CD44 is also found in several aggressive, but not low-grade, non-Hodgkin´s lymphomas (7) as well as in Hodgkin´s and nodal diffuse lymphomas.
- tonsil, skin cancer: variant CD44 isoform expression can be demonstrated in the plasma membrane of squamous cells of skin and tonsil epithelial and is greatly diminished in malignant squamous epithelial tumors.
- HIV: CD44 is almost completely depleted from the surface of HIV-infected cells.
- inflammatory joint diseases: CD44 expression was decreased in synovial fluid neutrophils from most patients.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)