Cat # changed from 633-07279 to 639-07271
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
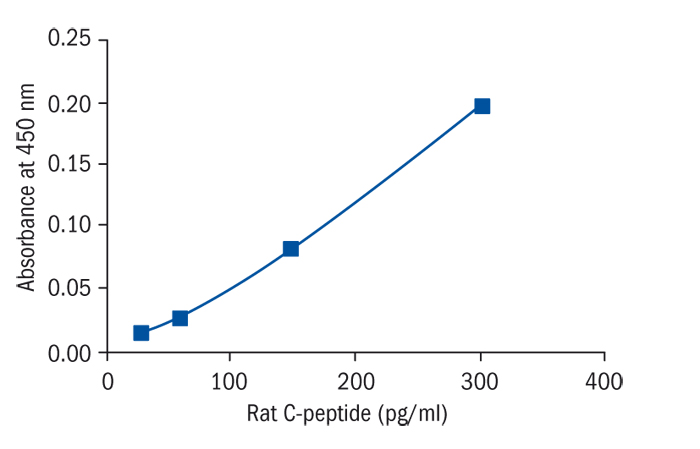
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
30–3 000 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
1.5 pg/ml
Research topic
Diabetology - Insulin, C-Peptide, Proinsulin, Animal studies
Summary
Insulin is first synthesized as a single chain polypeptide, proinsulin, then three disulfide bonds are formed, and finally divided into insulin and C-peptide through enzymatic splitting. Rat C-peptide 1 and 2 are both single chain peptides composed of 31 amino acids. Their homology is 93.5%. C-peptide is secreted together with insulin. The role of C-peptide has been considered to keep the best configuration to form three disulfide bonds, and has no biological activity, however, recent studies revealed that C-peptide can bind, probably, a G-protein-coupling specific receptor present on the surface of endothelial cells, kidney microtubule cells and fibroblasts, resulting in activation of calcium-dependent intracellular signaling, activation of Na+- K+-ATPase, and enhancement of NO synthesis. Administration of C-peptide to DM1 patients enhances blood circulation in the skeletal muscle and skin, and also minimizes kidney glomerular hyperfiltration, decreasing albumin excretion into urine, and also improves nervous function, indicating that C-peptide should be given together with insulin to DM1 patients. Important region to bind receptor has been reported to be C-terminal pentapeptide (27-31).
The biological half life of C-peptide is several times longer than that of insulin. Measurement of C-peptide is useful in estimation of pancreatic function for insulin synthesis and secretion. Urinary C-peptide concentration is well correlated to its blood level. C-peptide measurement is also useful in estimation of insulin secretion by cultured islet of Langerhans because very often insulin is added to the culture medium, and it is difficult to discriminate secreted insulin from added insulin. As Shibayagi’s kit recognizes the common sequences between C-peptide 1 and 2, it can measure total amount of C-peptide.
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Find documents for the lot