Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Description
The human Erythropoietin ELISA is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative detection of human Erythropoietin.
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
50 ul/well
Shipping
On blue ice packs. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store kit reagents between 2–8°C except controls. Store lyophilized controls at -20°C.
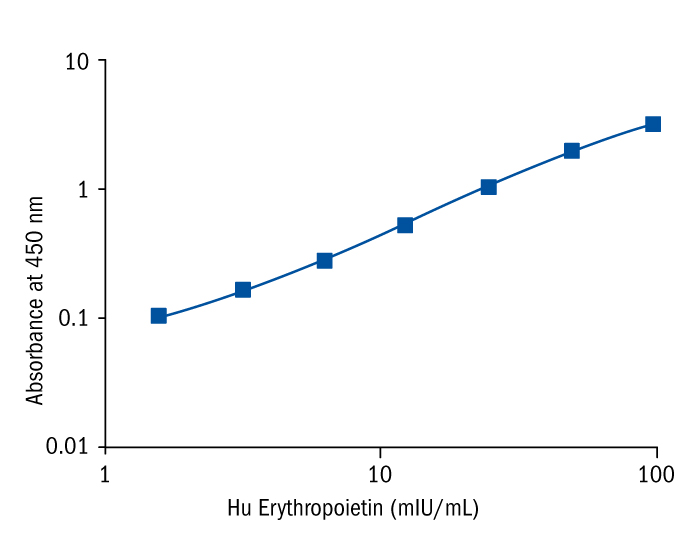
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
1.6–100 mIU/mL
Limit of Detection
0.14 mIU/mL
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 6.2%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 4.3%
Dilution Linearity
105,20%
Features
- RUO
- calibration range 1.6–100 mIU/mL
- limit of detection 0.14 mIU/mL
- intra-assay CV= 6.2%
- inter-assay CV= 4.3%
- lyophilized controls
Research topic
Bone and cartilage metabolism, Renal disease
Summary
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. EPO is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 34,000.
The kidney cells that make EPO are specialized and sensitive to low oxygen levels in the blood. These cells release EPO when the oxygen level is low in the kidney. EPO then stimulates the bone marrow to produce more red cells and thereby increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
EPO is the prime regulator of red blood cell production. Its major functions are to promote the differentiation and development of red blood cells and to initiate the production of hemoglobin, the molecule within red cells that transports oxygen.
The EPO gene has been found on Human chromosome 7 (in band 7q21). EPO is produced not only in the kidney but also, to a lesser extent, in the liver. Different DNA sequences flanking the EPO gene act to control kidney versus liver production of EPO.
The measurement of EPO in the blood is useful in the study of bone marrow disorders and kidney disease. Elevated levels of EPO can be seen in polycythemia, a disorder in which there is an excess of red blood cells. Lower than normal levels of EPO are seen in chronic renal failure.
EPO plays an important role in the brain's response to neuronal injury. EPO is also involved in the wound healing process.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)