Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
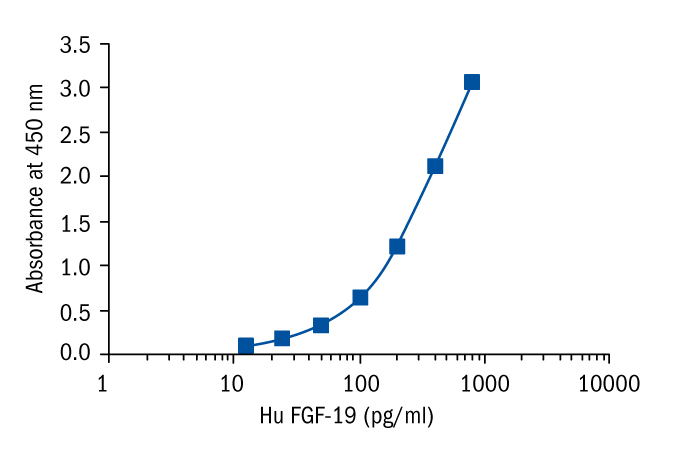
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
12.5–800 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
4.8 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 6.0%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 6; CV = 7.5%
Spiking Recovery
90,60%
Dilution Linearity
96,30%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Not tested
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- dog Not tested
- horse Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
- mouse Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- pig Not tested
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
- monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
Features
- It is intended for research use only
- The total assay time is less than 3.5 hours
- The kit measures FGF-19 in serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
- Assay format - 96 wells
- Standard and Quality Controls are recombinant protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
Research topic
Energy metabolism and body weight regulation
Summary
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are a large family of small (17-26 kDa) polypeptide growth factors found in organisms ranging from nematodes to humans. The FGF family has at least 22 members in vertebrates and share 13-71% amino acid identity. The initial characterization of these proteins focused on their ability to stimulate fibroblast proliferation. During embryonic development, FGFs have diverse roles in regulating cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. In the adult organism, FGFs are homeostatic factors and function in tissue repair and response to injury.
FGF signaling is mediated through one of four FGF receptors (FGFR1-FGFR4), a complex family of transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases. FGFR5 has also been described, but lacks the kinase domain and signaling capability. FGFs have a high affinity for heparin sulfate proteoglycans and require heparin sulfate to activate FGF receptors. Although multiple FGFs interact with each of the four FGFRs, a novel fibroblast growth factor FGF-19 exhibits exclusive binding to only one of FGF receptors (FGFR4).
The normal function of FGF-19 has not been resolved, although its role in inner ear development has been suggested. It has been also found that hepatocyte expression of FGF-19 is induced by the transcription factor, farnesoid X receptor (FXR). FXR is a key regulator of cholesterol metabolism through suppression of the catabolic enzyme cyp7a, the first and rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of bile acids (BA). A recent study found that, in humans, circulating FGF-19 has a diurnal rhythm controlled by the transintestinal BA flux, and that FGF-19 modulates hepatic BA synthesis. Through its systemic effects, circulating FGF-19 may also mediate other known BA-dependent effects on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
In transgenic mice expressing human FGF-19, researchers found a significant increased metabolic rate as well as decreased body weight and adiposity. Additionally, resistance to both diet-induced obesity and insulin desensitization were found. Similar responses have been observed when recombinant FGF-19 was injected into the mice. However, it has been shown too, that FGF-19 transgenic mice develop hepatic adrenocarcinomas with age, and recombinant FGF-19 treated mice exhibit proliferation of hepatocytes.
Areas of investigation:
Cholesterol metabolism, Metabolic syndrome
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)