Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma
Sample Requirements
75 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under this condition, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see the label on the box).
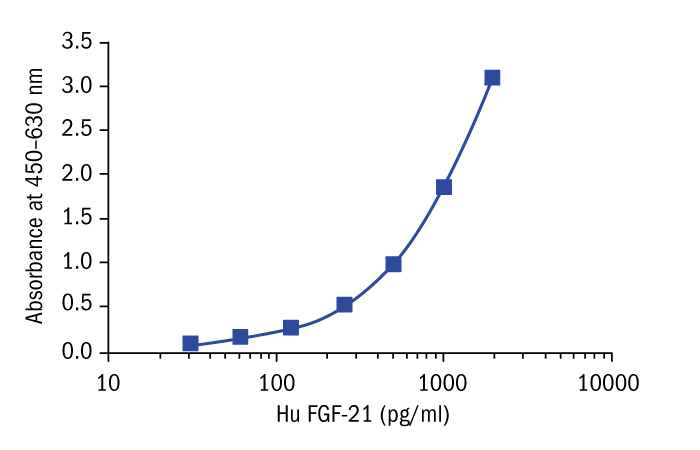
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
30–1920 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
7 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 6; CV = 2.0 %
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 6; CV = 3.3 %
Spiking Recovery
100.4 %
Dilution Linearity
102.1 %
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-detectable
- dog Non-detectable
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- mouse Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
- monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:2)
Features
- It is intended for research use only
- The total assay time is less than 3.5 hours
- The kit measures FGF-21 in serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
- Assay format - 96 wells
- Quality controls are human serum based
- Standard is recombinant protein based
- Components of kit are provided ready to use, concentrated, lyophilized or in liquid form
Research topic
Diabetology - Other Relevant Products, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation
Summary
The fibroblast growth factor family (FGFs) are a family of more than 20 small (17-26 kDa) secreted peptides. The initial characterisation of these proteins focused on their ability to stimulate fibroblast proliferation through FGF receptors (FGFRs). Members of FGFs family play important roles in defining and regulating the development and function of endocrine tissues as well as modulating various metabolic processes.
A recently described member of FGFs family, FGF-21, also called Fibroblast growth factor 21 precursor and UNQ3115/PRO10196, has been characterised as a potent metabolic regulator. FGF-21 is preferentially expressed in liver and regulates glucose uptake in human fat cells. Moreover, therapeutic administration of FGF-21 decreased plasma glucose levels and triglycerides to near normal levels in multiple mouse models of type 2 diabetes. Short-term treatment of normal or db/db mice with FGF-21 lowered plasma levels of insulin and improved glucose clearance compared with vehicle after oral glucose tolerance testing. Constant infusion of FGF-21 for 8 weeks in db/db mice nearly normalized fed blood glucose levels and increased plasma insulin levels. When administrated daily for 6 weeks to diabetic rhesus monkeys, FGF-21 caused dramatic decline in fasting plasma glucose, fructosamine, triglicerides, insulin, and glucagon. FGF-21 administration also led to significant improvements in lipoprotein profiles, including lowering of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and raising of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as well as beneficial changes in the circulating levels of several cardiovascular risk factors.
FGF-21, when overexpressed, protected animals from diet-induced obesity. These results define a functional role for FGF-21 in vivo and provide evidence that FGF-21 can lower glucose and triglyceride levels in diabetic animals.
In contrast to several members of the FGF family which may induce therapeutically undesirable in vivo proliferation of various cell types, a recent study demonstrated that FGF-21 did not induce mitogenicity, hypoglycemia or weight gain at any dose tested in diabetic or healthy animals or when overexpressed in transgenic mice. Thus, FGF-21 appears to have considerable potential for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Areas of investigation:
Lipid metabolism, Diabetes mellitus type 2, Metabolic syndrome
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)