Type
Polyclonal Antibody
Applications
Western blotting, ELISA, Immunohistochemistry
Antibodies Applications
Source of Antigen
E. coli
Hosts
Sheep
Preparation
The antibody was raised in sheep by immunization with the recombinant Human FGF-21.
Amino Acid Sequence
The immunization antigen (20.1 kDa) is a protein containing 195 AA of recombinant Human FGF-21. N-terminal His-tag, 14 extra AA.
MRGSHHHHHHGMASHPIPDSSPLLQFGGQVRQRYLYTDDAQQTEAHLEIREDGTVGGAADQSPESLLQLKALKPGVIQILGVKTSRFLCQRPDGALYGSLHFDPEACSFRELLLEDGYNVYQSEAHGLPLHLPGNKSPHRDPAPRGPARFLPLPGLPPAPPEPPGILAPQPPDVGSSDPLSMVGPSQGRSPSYAS
Species Reactivity
Human. Not yet tested in other species.
Purification Method
Immunoaffinity chromatography on a column with immobilized recombinant Human FGF-21.
Antibody Content
0.1 mg (determined by BCA method, BSA was used as a standard)
Formulation
The antibody is lyophilized in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.2.
Reconstitution
Add 0.2 ml of deionized water and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. Slight turbidity may occur after reconstitution, which does not affect activity of the antibody. In this case clarify the solution by centrifugation.
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
The lyophilized antibody remains stable and fully active until the expiry date when stored at -20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid repeated freezing/thawing cycles and store frozen at -80°C. Reconstituted antibody can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show decline in activity after one week at 4°C.
Quality Control Test
Indirect ELISA – to determine titer of the antibody
SDS PAGE – to determine purity of the antibody
BCA - to determine quantity of the antibody
Note
This product is for research use only.
Research topic
Diabetology - Other Relevant Products, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation
Summary
The FGFs are a family of more than 20 small (~17–26 kDa) secreted peptides. The initial characterization of these proteins focused on their ability to stimulate fibroblast proliferation. This mitogenic activity was mediated through FGF receptors (FGFRs) 1, 2, or 3. A fourth closely related tyrosine kinase receptor (FGFR4) was able to bind the FGFs but did not lead to a mitogenic response.
FGFs modulate cellular activity via at least 5 distinct subfamilies of high-affinity FGF receptors (FGFRs): FGFR-1, –2, –3, and –4, all with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and, except for FGFR-4, multiple splice isoforms, and FGFR-5, which lacks an intracellular kinase domain. There is growing evidence that FGFRs can be important for regulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis. The overexpression of a dominant negative form of FGFR-1 in β cells leads to diabetes in mice, which thus implies that proper FGF signaling is required for normal β cell function and glycemia maintenance. FGFR-2 appears to be a key molecule during pancreatic development. Moreover, FGFR-4 has been implicated in cholesterol metabolism and bile acid synthesis.
FGF-19, has been shown to cause resistance to diet-induced obesity and insulin desensitization and to improve insulin, glucose, and lipid profiles in diabetic rodents. Since these effects, at least in part, are mediated through the observed changes in metabolic rates, FGF-19 can be considered as a regulator of energy expenditure.
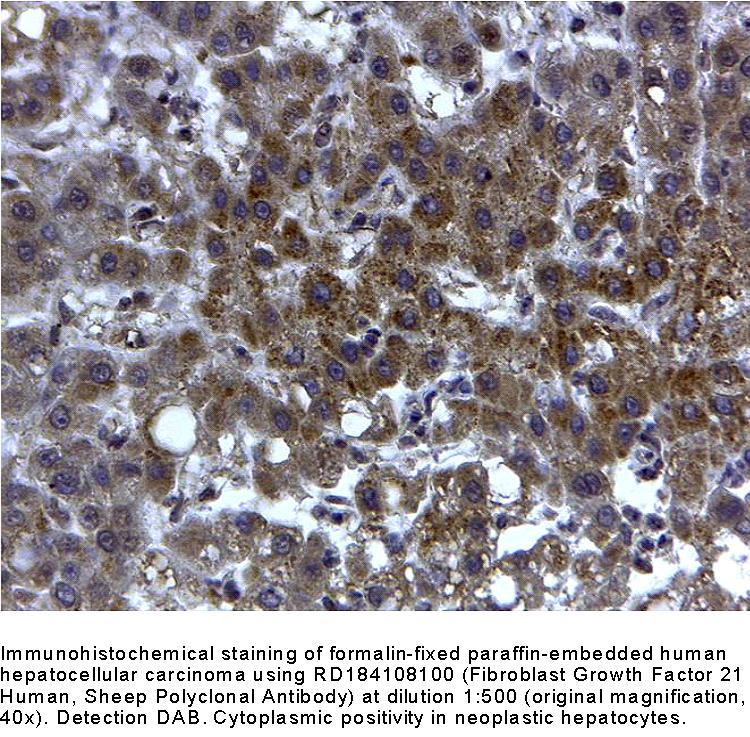
FGF-21 is preferentially expressed in liver, but an exact knowledge of FGF-21 bioactivity and its mode of action have been lacking to date. FGF-21 is a potent activator of glucose uptake on adipocytes, protects animals from diet-induced obesity when overexpressed in transgenic mice, and lowers blood glucose and triglyceride levels when therapeutically administered to diabetic rodents.