Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Urine, Amniotic fluid, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
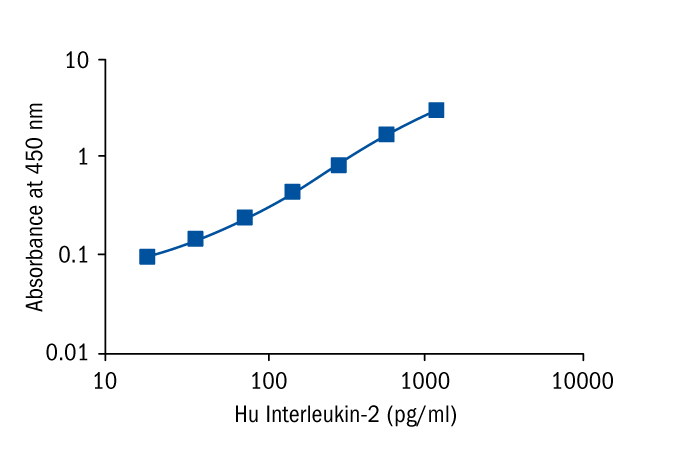
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
18.8–1200 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
9.1 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 7.0%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 5.0%
Research topic
Cytokines and chemokines and related molecules
Summary
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) plays a central role in the activation and proliferation of lymphocytes that have been primed by antigens. IL-2 plays a pivotal role in for the expansion of most T-cells, natural killer cells and B-cells during certain phases of their response.
IL-2 is a 15 kDa glycoprotein encoded by a single gene located in the q26-28 region of Human chromosome 4. The cDNA deduced polypeptide consists of 153 amino acids.
IL-2 gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional level by several activation pathways. Antigen-specific proliferation of helper and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes following stimulation is critically dependent on IL-2 expression, secretion, and binding to receptors for IL-2 induced in an autocrine fashion on the surface of T-cells.
Apart from its most important role to mediate antigen-specific
T-lymphocyte proliferation, IL-2 modulates the expression of IFN-g and major histocompatibility antigens, stimulates proliferation and differentiation of activated B-cells, augments natural killer cell activity and inhibits granulocyte-macrophage colony formation.
Alterations in the ability of T-cells to synthesize IL-2 have been observed in physiologic and pathologic states.
Because of the central role of IL-2 in immune response, IL-2 turned out to be a very important molecule for diagnostic and therapeutic implications.
IL-2 displays antitumoral effects, thus being used in cancer therapy.
Monitoring of IL-2 levels in serum provides more detailed insights in several pathological situations such as cancer, infectious diseases, transplant rejection, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and type I diabetes.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)