Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
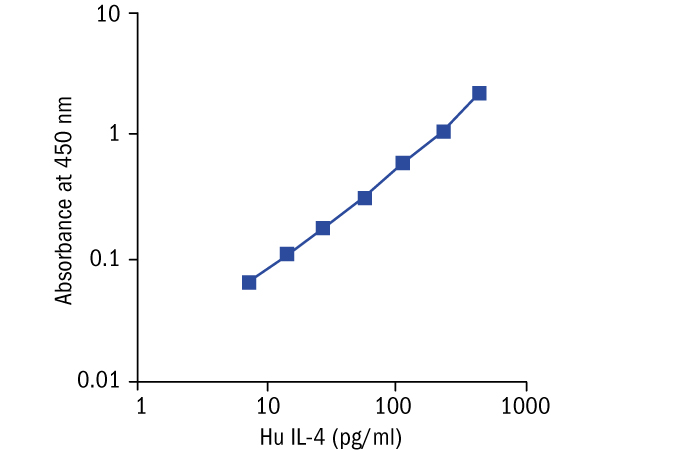
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
7.8–500 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
1.3 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 4.8%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 5.6%
Research topic
Cytokines and chemokines and related molecules
Summary
Human IL-4 exists in molecular weight forms between 15 and 19 kDa, representing variable glycosylation. The gene for Human IL-4 is found on the long arm of chromsome 5 in close association with genes for IL-13, IL-5 GM-CSF and IL-3.
IL-4 mediates its function by binding to receptors expressed on target cells. The IL-4 receptors exhibit an affinity of approximately 10-10 M. Receptors exist on freshly prepared B and T lymphocytes and macrophages, as well as on various cell lines including lymphoid cells, mast cell lines, a variety of other hematopoietic cell lines, fibroblasts and stromal cell lines. On T and B cells, receptors are present in low numbers (appr. 400), which are reported to be up-regulated by IL-2 and IL-4.
IL-4 is produced by a particular subset of T helper cells, the TH2 cells. These cells tend to make a specific set of lymphokines including IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, IL-3 and GM-CSF and fail to produce IL-2, IFNg, and lymphotoxin (TNFb). Apart from T cells, it has been shown that mast cells can produce IL-4.
IL-4 exerts numerous effects on various hematopoietic cell types. On B cells, IL-4 promotes immunological class switching to IgE and IgG1 isotypes and upregulates MHC class II and CD23 expression. It can promote survival, growth, and differentiation of both T and B lymphocytes, mast cells, and endothelial cells. In addition, IL-4 can inhibit the production of TNF, IL-1, and IL-6 by macrophages.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)