Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
35 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
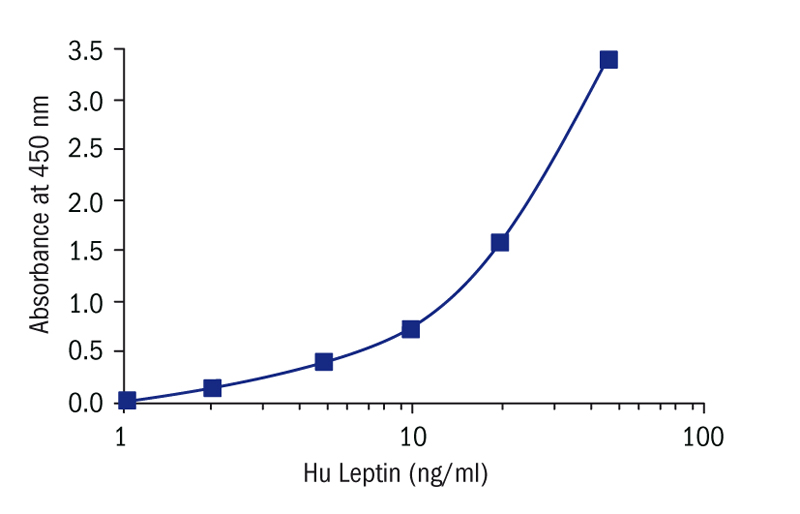
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
1-50 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.2 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n=8, CV = 5.9%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n=6, CV = 5.6%
Spiking Recovery
92.1%
Dilution Linearity
100.8%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-detectable
- dog Non-detectable
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- monkey Non-detectable
- mouse Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
Note
The kits are CE-IVD certified and intended for professional use.
More about Leptin on BioVendor Scientific Blog
Features
- European Union: for in vitro diagnostic use
- Rest of the world: for research use only!
- The total assay time is less than 2.5 hours
- The kit measures total leptin
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Quality Controls are human serum based
- Standards are recombinant protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
Research topic
Diabetology - Other Relevant Products, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation, Reproduction
Summary
Leptin, the product of the ob (obese) gene, is a single-chain 16 kDa protein consisting of 146
amino acid residues. Leptin is produced mainly in the adipose tissue, and is considered to play
an important role in appetite control, fat metabolism and body weight regulation. It targets the
central nervous system, particularly hypothalamus, affecting food intake. The primary effect of
leptin appears to be mediated by leptin receptors expressed mainly in the hypothalamus. In
humans, leptin levels correlate with body mass index (BMI) and percentage body fat, and are
elevated even in obese individuals. Leptin has a dual action; it decreases the appetite and
increases energy consumption, causing more fat to be burned. Leptin is secreted in circadian
fashion with nocturnal rise in both lean and obese patients.
Mutations of the ob gene resulting in leptin deficiency are the cause of obesity in the ob/ob
mice. Endogeneous leptin can normalize their body weight. In contrast, high levels of leptin in
obese human subjects point to an insensitivity to endogeneous leptin.
Other factors in addition to the amount of body fat appear to regulate leptin action: insulin,
glucocorticoids, catecholamines and sex hormones. Studies have shown that leptin may be
linked to reproductive function.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Product Brochure
CE IVD Assays
Other Documents
Declaration of Conformity