Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
7 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
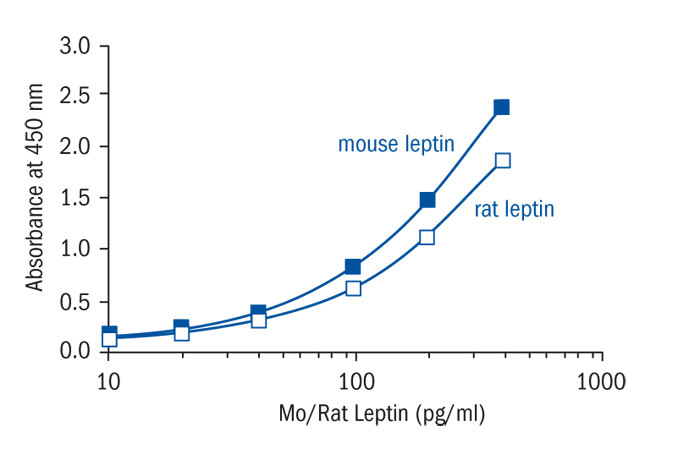
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
100–4000 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
Analytical Limit of Detection is calculated from the real leptin values in wells and is 30 pg/ml for mouse leptin and 50 pg/ml for rat leptin
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 2.2%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 8; CV = 3.4%
Spiking Recovery
94,50%
Dilution Linearity
96,70%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-detectable
- dog Non-detectable
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- monkey Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- sheep Not tested
- chicken Not tested
- mouse Yes
- rat Yes
- human Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
Features
- The total assay time is less than four hours.
- The kit measures total serum leptin.
- Quality controls are mouse and rat serum based. No human sera are used.
Research topic
Diabetology - Other Relevant Products, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation, Reproduction, Animal studies
Summary
Leptin is a protein hormone with important effects in metabolism and regulating body weight. It is a single-chain 16 kDa protein consisting of 146 amino acid residues and encoded by the obese (ob) gene.
Leptin is expressed predominantly by adipocytes, small amounts of leptin are also secreted by cells in the epithelium of stomach and in the placenta. Leptin´s effect on body weight is mediated through effects on hypothalamic centers, where leptin receptors are highly expressed. Leptin has a dual action, it decreases the appetite and increases energy consumption.
A mutations in the ob gene of leptin or in the gene of leptin receptor causes hyperphagia, reduced energy expenditure, and severe obesity in the ob/ob mice.
Ob gene knockout mice are also characterized by several metabolic abnormalities including hyperglucocorticoidemia, hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance.
When ob/ob mice are treated with injections of leptin, they lose their excess fat and return to normal body weight.
Studies have shown that leptin appears to be a significant regulator of reproductive function. In addition, leptin is involved in bone metabolism and plays a significant role as an immunomodulator.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)