Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Amniotic fluid, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
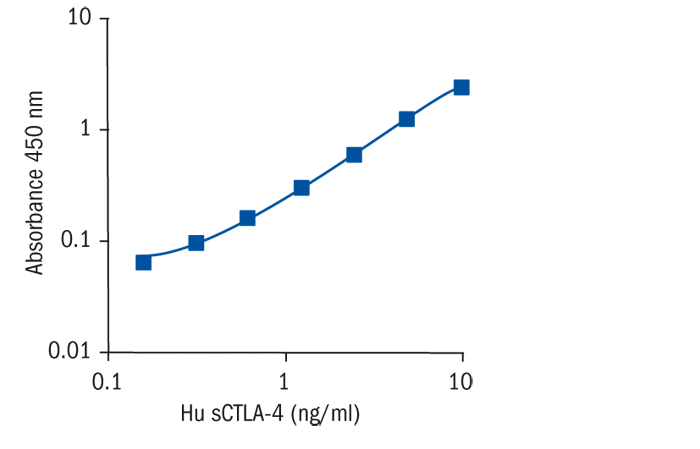
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.16–10 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.13 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 4.8%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 10.4%
Spiking Recovery
78,00%
Dilution Linearity
110,00%
Research topic
Cell surface proteins (sCD), Transplantation
Summary
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated gene –4 (CTLA-4) was initially described as a classical type I glycoprotein on the surface of activated T-cells (1). CTLA-4 is a member of the Ig gene superfamily and along with its homologue, CD28, is a B7 binding protein. There is evidence that CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell activation, ligation of CTLA-4 on the T-cell surface initiates a series of biochemical events that attenuate an ongoing immune response .
CTLA-4 knock out mice demonstrate profound polyclonal lymphoproliferative disoders that infiltrate most major organ systems and the animals die a few weeks after birth. The animals have increased levels of IgG which illustrates the role of CTLA-4 on humoral immune responses as well.
A role for CTLA-4 in autoimmune disease is suggested by the observations that blockade of B7/CTLA-4 interaction exacerbates animal models of autoimmune disease such as experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and diabetes. A search for genetic markers that segregate with Graves‘ disease revealed an association with CTLA-4 polymorphisms. CTLA-4 is further more closely linked to autoimmune thyroid disease (ATD). A native soluble form of CTLA-4 has been described to be present in human serum . A correlation of circulating CTLA-4 and ATD has been shown.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)