Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
20 µl (1:6 prediluted)
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
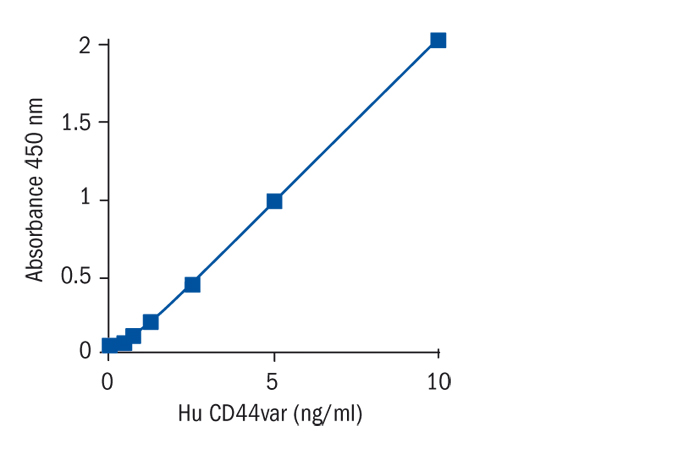
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.32–10 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.14 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 3.6%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 5.8%
Spiking Recovery
92,00%
Dilution Linearity
110,00%
Research topic
Cell adhesion proteins, Cell surface proteins (sCD), Extracellular matrix, Oncology
Summary
CD44 (Pgp-1; Ly-24; ECMR III; F10-44-2; H-CAM; HUTCH-I; In(Lu)- related p80; Hermes antigen; hyaluronan receptor) is a polymorphic glycoprotein which participates in a wide variety of cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions including lymphocyte homing, establishment of B and T cell immune responses, tumor metastasis formation and inflammation.
Three isoform categories of the CD44 molecule have been identified:
- a predominant 80-90 kDa category, the so-called standard form named CD44std,
- an intermediate size category of 110-160 kDa and
- a category which includes very large isoforms of 250 kDa covalently modified by the addition of chondroitin sulfate (15).
This CD44-family of transmembrane receptor molecules is derived from a single gene located on chromosome 11. Alternative splicing of the mRNA gives rise to the different isoforms, containing inserts of varying sizes in the extracellular domain of the molecule (exons v2-v10). All CD44 isoforms are variably glycosylated. In contrast to standard CD44 (CD44std) which is almost ubiquitously expressed, the variety of CD44 isoforms (CD44var) have a much more restricted distribution, e.g., on keratinocytes (exons v3-v10), epithelial cells (exons v(-v10), activated lymphocytes and macrophages (exon v6).
A splice variant of CD44 (exons v4-v7) confers metastatic behavior in a rat carcinoma model; aberrant expression of splice variants has been detected on a variety of human tumor cell lines as well as
primary and metastatic human tumors, including lymphomas, carcinomas (colon, thyroid, mamma, bladder), and gliomas. Detection of abnormal regulation of CD44 splicing thus could be helpful in cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. The sCD44var(v5) ELISA detects all circulating CD44 isoforms comprising the sCD44var(v5) sequences.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)