Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Urine, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
50 µl (1:100 prediluted)
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
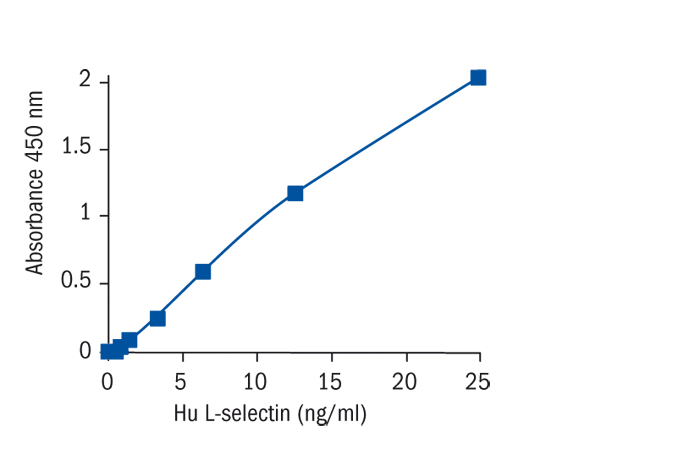
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.39–25 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.19 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 3.7%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 4.2%
Spiking Recovery
99,00%
Dilution Linearity
89,10%
Research topic
Cell adhesion proteins, Oncology
Summary
Determination of soluble/circulating L-selectin could provide more detailed insights into the pathological modifications during various diseases:
- allergy: L-selectin expression is down-modulated on eosinophils recovered from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after allergen provocation.
- bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): BAL transiently promotes PMN/monocyte activation and recruitment to the bronchoalveolar space. The cells respond with a complete shedding of L-selectin when they extravasate from the blood into the bronchoalveolar space.
- deep venous thrombosis (DVT): A case can be made for the participation of PMN's in the initiation and propagation of venous thrombosis. Probably via L-selectin leukocytes adhere to areas of veins that serve as sites for initiation of thrombi.
- HIV: patients suffering from HIV-infection showed markedly elevated levels of sL-selectin in serum.
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM): serum levels of L-selectin were found to be elevated in IDDM patients and in subjects at risk for developing IDDM.
- Kawasaki Syndrome: sL-selectin levels seem to be less than those of normals.
- malignant B-cell populations: B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, hairy cell leukaemia and mantle zone lymphoma are L-selectin positive.
- neonatal bacterial infection: in case of intra-uterine infection lymphocytes obtained from cord blood have a diminished L-selectin expression. This is independent of gestational age, birth weight, umbilical artery pH, hematocrit, leukocyte count, absolute neutrophil count, CRP-level or maternal fever .
- sepsis: patients suffering from sepsis showed markedly elevated levels of sL-selectin in serum. Vascular endothelial injury observed in overwhelming sepsis may be caused by neutrophil-derived enzymes. Adherence to endothelium is a prerequisite for this process. Measurement of sL-selectin may provide further insights into the interrelationship between neutrophil activation and endothelial damage in gram-negative sepsis.
- surgery: patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery may develop an acute post-operative capillary leak, due to endothelial injury inflicted by adherent neutrophils. In those patients L-selectin is completely lost in a small but progressively increasing proportion of PMN's, which could be responsible for the endothelial damage.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)