Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
20 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
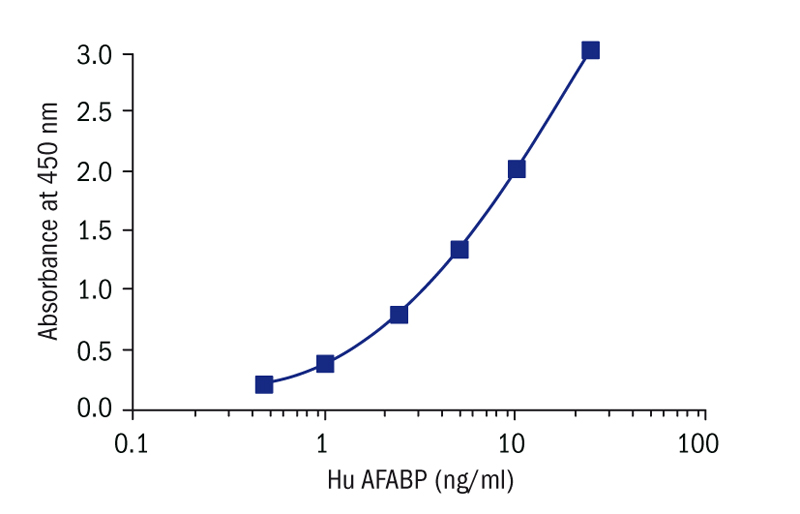
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.5–25 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.05 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 2.5%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 3; CV = 3.9%
Spiking Recovery
104,60%
Dilution Linearity
100,20%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat None-specific binding
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- dog Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
- mouse Yes
- monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
Note
The kits are CE-IVD certified and intended for professional use.
Features
- It is intended for research use only
- The total assay time is less than 4 hours
- The kit measures total AFABP in serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Quality Controls are human serum based
- Standard is recombinant protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
- EU Patent Number: EP1904082
Research topic
Diabetology - Other Relevant Products, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation
Summary
Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein AFABP is a 15 kDa member of the intracellular fatty acid binding protein (FABP) family, which is known for the ability to bind fatty acids and related compounds (bile acids or retinoids) in an internal cavity. AFABP is expressed in a differentiation-dependent fashion in adipocytes and is a critical gene in the regulation of the biological function of these cells. In mice, targeted mutations in FABP4 (mouse gene is also called aP2 and its relevant protein P2 adipocyte protein or 3T3-L1 lipid binding protein) provide significant protection from hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in the context of both dietary and genetic obesity. Adipocytes obtained from AFABP-deficient mice also have reduced efficiency of lipolysis in vitro and in vivo, and these mice exhibited moderately improved systemic dyslipidemia. Recent studies also demonstrated AFABP expression in human macrophages upon differentiation and activation. In these cells, AFABP modulates inflammatory responses and cholesterol ester accumulation, and total or macrophage-specific AFABP deficiency confers dramatic protection against atherosclerosis in the apoE-/- mice. These results indicate a central role for AFABP in the development of major components of the metabolic syndrome through its distinct actions in adipocytes and macrophages.
Besides being active within the cell, AFABP appears to be a secreted protein (for normal levels and correlations with certain metabolic parameters see chapter 15). The extracellular role of secreted AFABP remains to be determined.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Product Brochure
CE IVD Assays
Other Documents
Declaration of Conformity