Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Description
The human Cu/ZnSOD ELISA is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative detection of human Cu/ZnSOD. The human Cu/ZnSOD ELISA is for research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Applications
Serum, Urine, Amniotic fluid, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant, Fetal umbilical vein blood
Sample Requirements
10 µl (1:20 prediluted)
Shipping
On blue ice packs. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
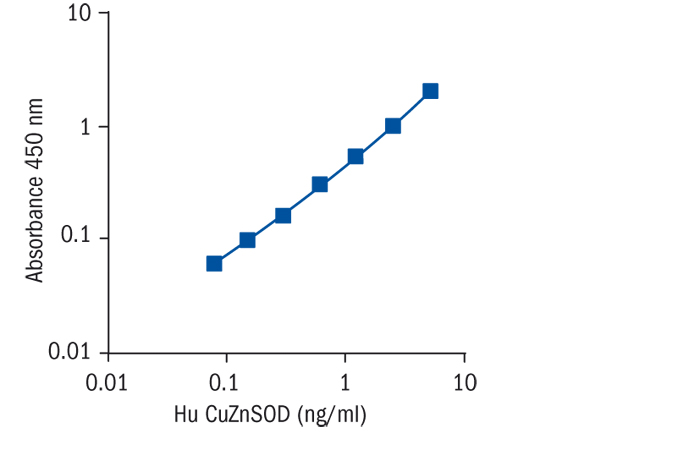
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.08–5 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.04 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 5.1%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 5.8%
Spiking Recovery
98,00%
Dilution Linearity
90,00%
Features
- RUO
- calibration range 0.8 - 5 ng/ml
- The limit of detection is 0.04 ng/ml
- intra-assay CV = 5.1%
- inter-assay CV = 5.8%
Research topic
Oxidative stress
Summary
Superoxide Dismutases (SODs) (E.C.1.15.1.1.) are a unique family of metalloproteins that catalyze the dismutation of superoxide anion radicals (O2-) to oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
O2- + O2- + 2H+ => H2O2 + O2
SOD is ubiquitous in oxygen metabolizing cells protecting these cells against direct and indirect oxygen-mediated free radical damage. Four types of SOD have been defined on the basis of distinctions in their metal cofactors and distribution: Manganese (MnSOD) principally located in the matrix of mitochondria of all aerobes, copper/zinc (Cu/ZnSOD) mainly present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, iron (FeSOD), predominantly in the cytosol, chloropasts or mitochondria of prokaryotes as well as extracellular (ECSOD), which is found in the extracellular fluids or membrane associated in mammals.
The properties of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase are quite different from those of the manganese or iron enzymes. Sequence analysis has indicated a homology between Mn and Fe class enzymes but these have no homology with the Cu/Zn enzyme. The human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase is a dimeric protein composed of 2 subunits of 153 amino acid residues and a molecular weight of 16 kDa each. Dissociation of the subunits is facilitated by alkylation of the two sulfhydryl groups in the protein or by removal of the copper and zinc ions.
The human Cu/ZnSOD gene has been localized to chromosome 21q22.1.
Cu/ZnSOD gene expression is induced by mediators of oxidative stress like sulfhydryl antioxidants, interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor. Constitutive expression of copper and zinc SOD mRNA is highest in dividing cells.
Induction of Cu/ZnSOD expression resulting in elevated levels of Cu/ZnSOD in human body fluids is of diagnostic value for measuring the activity of different diseases.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)