Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Cerebrospinal fluid, Tissue extract, Plasma
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
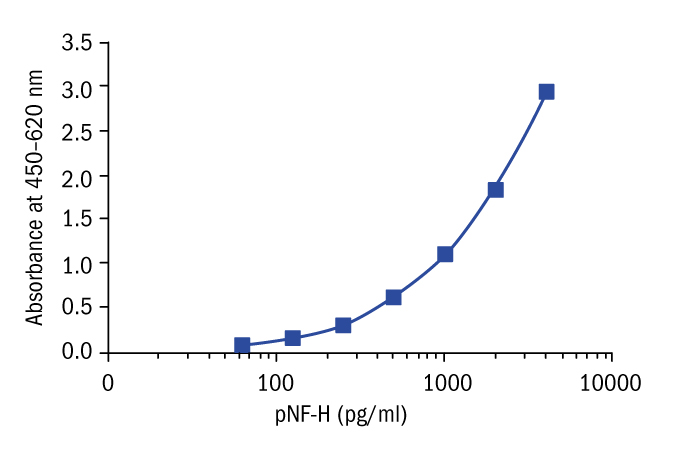
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
62.5–4000 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
23.5 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 4.5%
Spiking Recovery
CSF sample: 98.8%
Serum sample: 95.8%
Dilution Linearity
CSF sample: 106.1%
Serum sample: 105.5%
Features
- It is intended for research use only.
- The total assay time is less than 4 hours.
- The kit measures pNF-H in serum, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and tissue samples
- Assay format is 96 wells.
- Standard and Quality Controls are human brain extract based. No animal sera are used.
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized.
Research topic
Neural tissue markers, Oncology
Summary
Neurofilaments are the 10nm diameter filaments which are the most abundant protein components of neurons and are particularly concentrated in axons. They belong to the intermediate or 10nm filament protein/gene superfamily which also includes keratins, the major structural proteins of skin. Neurofilaments (NF) consist predominantly of three subunits:, NF-L (low), NF-M (medium), and NF-H (heavy or high). NF-H protein is about 200 kDa and contains unusual multiple repeated sequence lysine-serine-proline (KSP), and in axonal neurofilaments essentially all serine residues are heavily phosphorylated. Because phosphorylated forms of NFH (pNF-H) are quite resistant to proteases, pNF-H released from damaged and diseased axons should remain in fluid undegraded. This means that detection of pNF-H in blood and CSF points unambiguously to neuronal damage due to the fact that pNF-H is found exclusively in neurons.
This protein can be detected in quite large amounts following experimental spinal cord and brain injury in rats. Levels of greater than 100 ng/ml of pNF-H were detectable in blood following serious cord injury and lower, but still easily detectable levels, were found in blood of animals given experimental brain injury. In recently studies with rats subjected to traumatic brain injury (TBI) using a controlled cortical impact (CCI) device, elevated blood pNF-H levels were found. Results show time-dependent changes in the detectable pNF-H levels and these levels correspond with the severity of the injury and the amount of cortical damage.
Studies with mice transgenic for mutations of human copper/zinc superoxide dismutase 1 which are associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) have revealed corresponding increased amounts of pNF-H in blood of these animals. These mice develop axonal degeneration pathology similar to that seen in humans with ALS, and blood pNF-H levels can be used to monitor this degeneration. Interestingly, pNF-H is detectable before the onset of obvious disease symptoms.
Other experiments have shown that pNF-H is detected in the plasma of humans suffering from optic neuritis and in elevated levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of individuals suffering from brain tumors and stroke.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)