Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Cerebrospinal fluid, Saliva, Plasma
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, assay components are stable till the expiry date is over. (See the expiry date indicated on the kit label).
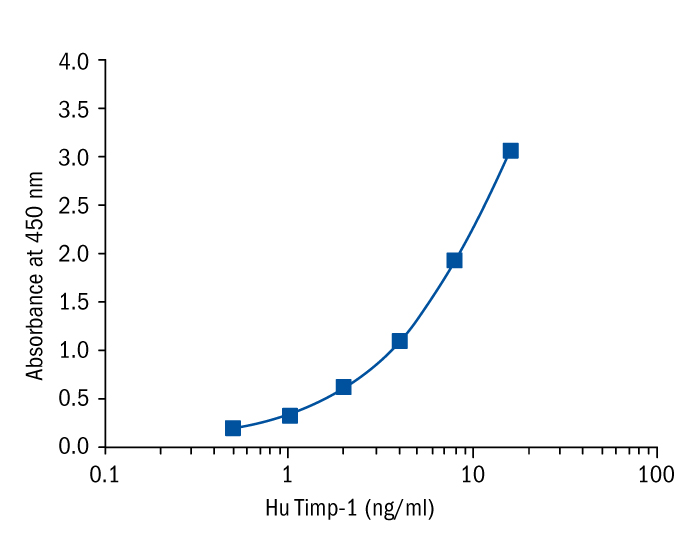
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.5–16 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 5%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 6; CV = 7%
Spiking Recovery
99,65%
Dilution Linearity
98,17%
Features
- It is intended for research use only
- The total assay time is less than 2.5 hours
- The kit measures TIMP-1 in serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparine), saliva and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Standard is recombinant protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
Research topic
Extracellular matrix, Others
Summary
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), located on chromosome Xp11.3-p11.23, belongs to the Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases family which includes four identified members (TIMP-1, TIMP-2, TIMP-3, and TIMP-4). TIMP-1 encodes a 931 base-pair mRNA and a 207 amino acid protein. Studies have shown that this protein may inhibit the proteolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) by forming noncovalent 1:1 stoichiometric complexes and regulates the balance of matrix remodeling during degradation of extracellular matrix.
TIMP-1 has been implicated in a number of other biological processes, including growth factor activity, tissue remodeling, inhibition of angiogenesis, changes in cell morphology, and stimulation of gonadal steroidogenesis. In the CNS, TIMP-1 provides neuroprotective effects through its role in blood–brain barrier maintenance, which is accomplished by interacting with ECM components, inhibiting MMPs, and reducing glutamate-mediated calcium influx following excitotoxic stress. In the context of brain pathogenesis, TIMP-1 is linked to diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and human brain tumors.
Recently, clinical studies have shown that the aberrant expression of TIMP-1 is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in a series of tumors, such as gastric cancer, papillary thyroid carcinoma, cutaneous melanoma, breast cancer lung and colorectal cancers. Interestingly, in severe sepsis, the expression level of TIMP-1 is significantly elevated. MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and IL-6 plasma levels were measured in patients with severe sepsis and TIMP-1 showed the highest sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value for sepsis prognosis, confirming TIMP-1 as a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with severe sepsis.
Matrix metalloproteinases are indispensable elements of tissue reconstruction. MMPs released from macrophages lead to the destruction of elastin and cause emphysema. These enzymes participate in normal body functions but they behave differently in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The genetic polymorphisms of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 are the tissue inhibitors of MMPs that have been found to be associated with COPD. Another recent study demonstrated that TIMP-1 is present at high levels in sera from patients with tuberculosis (TB), and that expression of TIMP-1 mRNA is induced by mycobacteria. TIMP-1 may therefore be a potential biomarker of tuberculosis in humans.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)