Cat # changed from RSCYK190R to YK190
Type
Competitive ELISA, Immobilized antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma
Sample Requirements
20 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
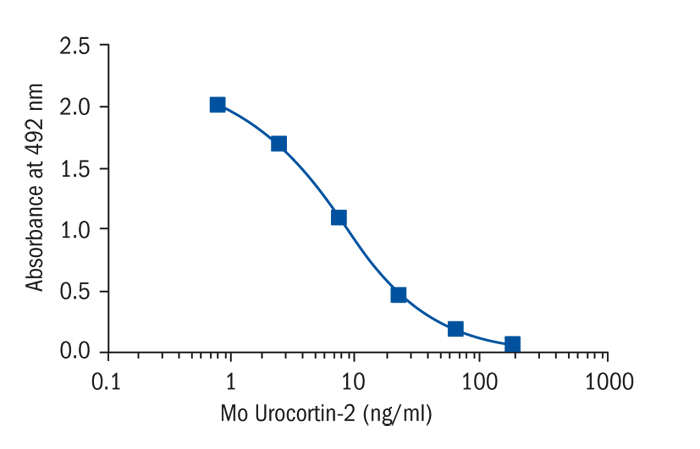
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.82–200 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
Mouse plasma: CV = 2.5-5.3%
Mouse serum: CV = 6.7-9.0%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
Mouse plasma: CV = 4.7-8.3%
Mouse serum: CV = 6.4-11.1%
Spiking Recovery
Mouse plasma: 107.8%
Mouse serum: 121.7%
Research topic
Animal studies
Summary
Urocortin 2 (Ucn 2), also known as stresscopin-related peptide, is a novel predicted neuropeptide related to
corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF). The peptide consisting of 38 amino acid residues was first demonstrated to be expressed centrally and to bind selectively to type 2 CRF receptor (CRFR2). In the rodent, Ucn 2 transcripts were shown to be expressed in the discrete regions of the central nervous system including stress-related cell groups in the hypothalamus and brainstem. More recently, the expression of Ucn 2 transcripts was detected in the olfactory bulb, pituitary, cortex, hypothalamus, and spinal cord. Ucn 2 mRNA was also found to be expressed widely in a variety of peripheral tissues, most highly in the skin and skeletal muscle tissues. Ucn 2-like immunoreactivity was detected by RIA in acid extracts of mouse brain, muscle, and skin. Immunohistochemically Ucn 2 was found in both skin epidermis and adnexal structures and in the skeletal muscle myocytes. Ucn 2 gene transcription was stimulated in the hypothalamus and brainstem by glucocorticoid administration to the mouse and inhibited by removal of glucocorticoids by adrenalectomy, suggesting a putative link between the CRFR1 and CRFR2 pathways. On the other hand, in the rat a stressor-specific regulation of Ucn 2 mRNA expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus was demonstrated, which raised the possibility of a modulary role of Ucn 2 mRNA in stress-induced alteration of anterior and posterior pituitary function, depending on the type of stress. Administration of dexamethasone to the
mouse resulted in a decrease of Ucn 2 mRNA levels in the back skin region. Adrenalectomy signifcantly increased Ucn 2 mRNA levels in the skin, and the levels were reduced back to normal levels after corticoid replacement. CRFR2 is found in cardiomyocytes and in endothelial and smooth muscle cells of the systemic vasculature. Ucn 2 is expressed in the mouse cardiomyocytes. In the mouse, Ucn 2 treatment augmented heart rate, exhibited potent inotropic and lusitropic actions on the left ventricle, and induced a downward shift of the diastolic pressure-volume relation. Ucn 2 also reduced systemic arterial pressure, associated with a lowering of systemic arterial elastance and systemic vascular resistance. The effects of Ucn 2 were specific to CRFR2 function and independent of beta-adrenergic receptors. These experiments demonstrated the potent cardiovascular physiologic actions of Ucn 2 in the both wild-type and cardiomyopathic mice and support a potential beneficial use of Ucn 2 in congestive heart failure treatment. The use of Ucn 2 was also proposed to treat ischemic heart disease because of its potent cardioprotective effect in the mouse heart and its minimal impact on the hypothalamic stress axis. Administration of Ucn 2 to the mouse prevented the loss of skeletal muscle mass resulting from disuse due to casting, corticosteroid treatment, and nerve damage. In addition, Ucn 2 treatment prevented the loss of skeletal muscle force and myocyte cross-sectional area that accompanied muscle mass losses resulting from disuse due to casting. In normal muscles of the mouse, Ucn 2 increased skeletal muscle mass and force. It was thus proposed that Ucn 2 might find utility in the treatment of skeletal muscle wasting diseases including age-related muscle loss or sarcopenia. Mouse urocortin 2 (Ucn 2) is a new peptide predicted from mouse cDNA sequence and its physiologic and pathophysiologic significance has not yet been fully elucidated. However, the experimental data presented to date provided evidence for the important physiologic roles of Ucn 2 and urge the necessity of further investigation of the peptide from various points of view.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)