Product has been modified
Clara Cell Protein Human ELISA has been renamed to Club Cell Protein (CC16) Human ELISA. This change respects a name-change policy of the major respiratory journals (including the journals of the American Thoracic Society, the European Respiratory Society and the American College of Chest Physicians) that went into effect beginning January 1, 2013.
Should you have any question, please contact the Technical Support Department.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
5 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
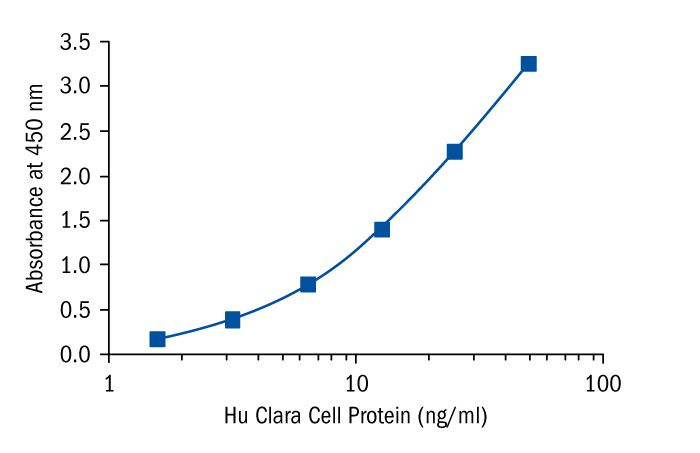
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
1.57–50 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
46 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 3.4%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 4; CV = 4.7%
Spiking Recovery
96,00%
Dilution Linearity
103,60%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-detectable
- dog Non-detectable
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- monkey Yes
- mouse Yes
- human Yes
Note
The kits are CE-IVD certified and intended for professional use.
Features
- European Union: for in vitro diagnostic use
- Rest of the world: for research use only!
- The total assay time is less than 4 hours
- The kit measures total Club cell protein in serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Quality Controls are human serum based
- Standard is recombinant protein (E. coli) based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
Clinical use and areas of investigation:
- Pneumonia and bronchopneumonia
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis
- Acute lung injury
- Asthma and allergic rhinitis
- Lung cancer
- IgA-nephropathy
Research topic
Immune Response, Infection and Inflammation, Pulmonary diseases, COVID-19
Summary
Human Club cell protein (CC16, CC10, uteroglobin, urinary protein 1 or Clara cell secretory
protein) is a member of the secretoglobin family of proteins and is a secreted product of nonciliated
bronchiolar Club cells. Its function remains to be fully elucidated but there is
convincing data suggesting its role as an immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory agent.
Club cell protein inhibits phospholipase A2 activity as well as interferon gamma signaling and
Th1 vs. Th2 lymphocyte regulation.
Club cell protein concentrations have been determined in serum, plasma and bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid in numerous studies since 1994. In serum, its increase is associated with age and
asbestos, nitrogen chloride and ozone exposure. Higher levels of CC16 were demonstrated in
patients with sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis and high PEEP ventilation. Decreased serum
CC16 levels are found after pulmonary resection in smokers and in subjects with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma or silica exposure.
Decreased CC16 concentrations were also found in the amniotic fluid of fetuses suffering from
pulmonary hypoplasia caused by various mechanisms (diaphragmatic hernia, diabetic
fetopathy, Turner and Down syndrome). In pleural effusions, the CC16 concentration appears
to be associated with its diffusion from the lung as evidenced by high CC16 levels in cardiac
pleural congestion.
Based on the above reports Club cell protein might be perspective useful diagnostic marker of
pulmonary diseases and injuries.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)
Product Brochure
CE IVD Assays
Other Documents
Declaration of Conformity

 ELISA_v2.png?size=160x150&quality=70)