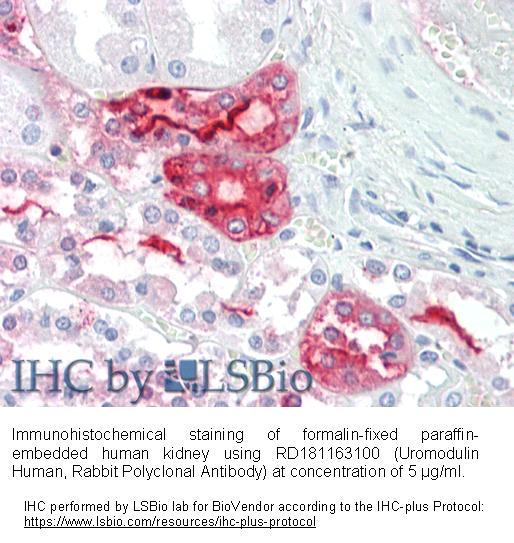
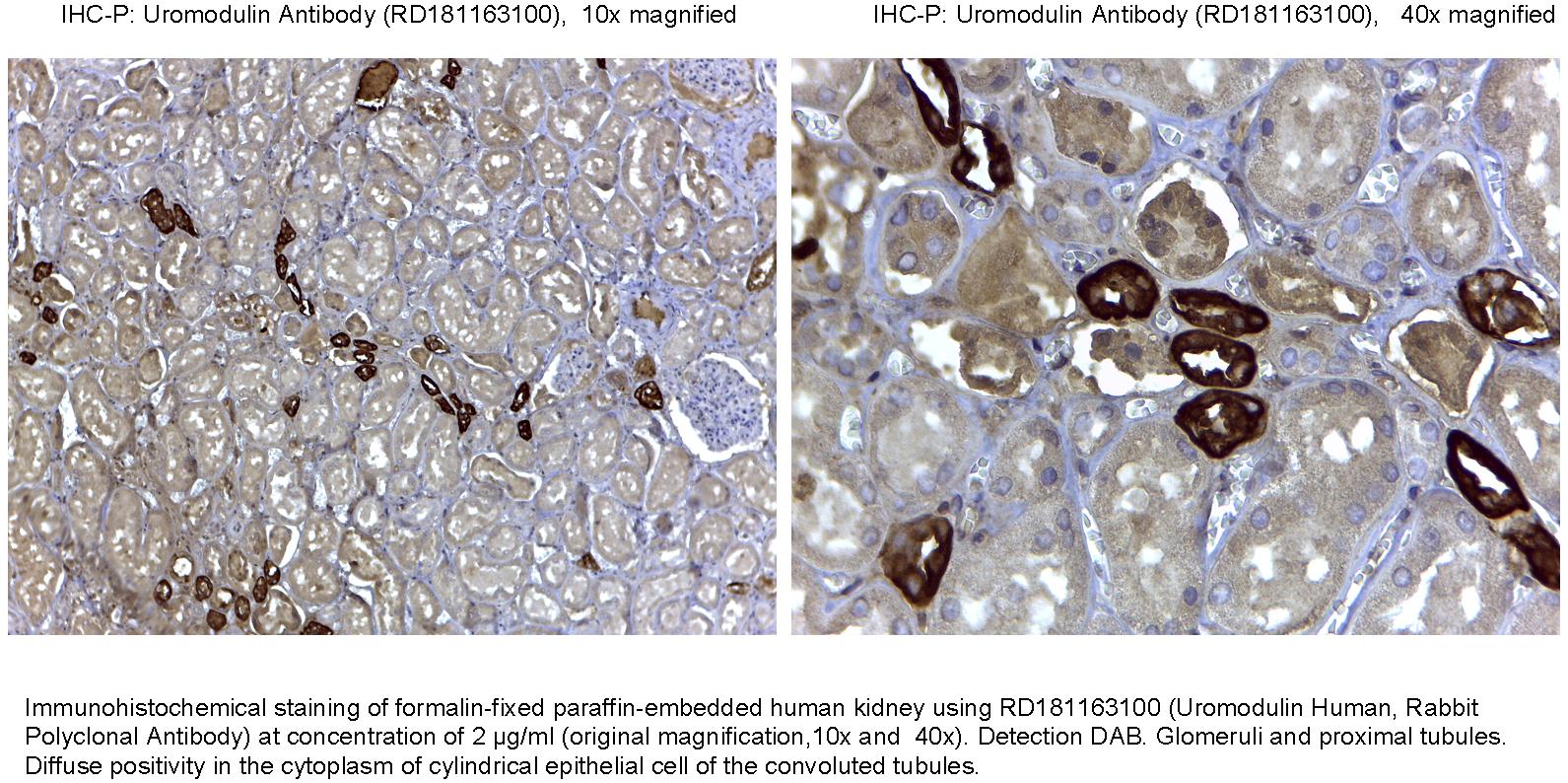
Type
Polyclonal Antibody
Applications
Western blotting, ELISA, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation
Antibodies Applications
Source of Antigen
Human urine
Hosts
Rabbit
Preparation
The antibody was raised in rabbits by immunization with the native Human Uromodulin (urine).
Species Reactivity
Human. Not yet tested in other species.
Purification Method
Immunoaffinity chromatography on a column with immobilized native Human Uromodulin (urine).
Antibody Content
0.1 mg (determined by BCA method, BSA was used as a standard)
Formulation
The antibody is lyophilized in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.2.
Reconstitution
Add 0.2 ml of deionized water and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. Slight turbidity may occur after reconstitution, which does not affect activity of the antibody. In this case clarify the solution by centrifugation.
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
The lyophilized antibody remains stable and fully active until the expiry date when stored at -20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid repeated freezing/thawing cycles and store frozen at -80°C. Reconstituted antibody can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show decline in activity after one week at 4°C.
Quality Control Test
Indirect ELISA – to determine titer of the antibody
SDS PAGE – to determine purity of the antibody
BCA - to determine quantity of the antibody
Note
This product is intended for research use only.
Research topic
Renal disease
Summary
Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall protein, UMOD) is approx. 85-kDa glycoprotein that is produced in the thick ascending limb of Henle´s loop and early distal convoluted tubules of the nephron. It is a transmembrane protein, which is secreted into the urine through proteolytic cleavage of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. It belongs to the GPI family. Healthy individuals excrete tens of miligrams of uromodulin per day, making in the most abundant protein in the urine. Uromodulin modulates cell adhesion and signal transduction by interacting with cytokines and it inhibits the aggregation of calcium crystals. By reducing calcium oxalate precipitation, uromodulin plays a protective role with respect to renal stone formation as demonstrated by recent studies on THP- deficient mice prone to nephrolithiasis. THP acts as a host defense factor against urinary tract infections induced by uropathogens such as Esherichia coli, Staphylococcus saphrophyticus, Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiela pneumonie. Uromodulin binds to type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli and thereby blocks colonization of urothelial cells. Tamm-Horsfall protein interacts with other molecules and cells including IL-1, IL-2, TNF, IgG, neuthrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes. Binding of uromodulin to neutrophils induces synthesis of IL-8, provokes the respiratory burst and degranulation and stimulates chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Recently, genome-wide association studies identified uromodulin as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Mutations in the Uromodulin gene are associated with three autosomal dominant tubulo-interstitial nephropathies such as familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (FJHN), medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD2) and glomerulocystic kidney disease (GCKD). These disorders are characterized by juvenile onset of hyperuricemia, gout and progressive renal failure.