Successful participation in EQA!
We are pleased to announce that we have successfully participated in the External Quality Assessment (INSTAND, survey of March 15, 2024), being involved in determination of Cystatin C.
Please find the Certificate in Docs.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Urine, Cerebrospinal fluid
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
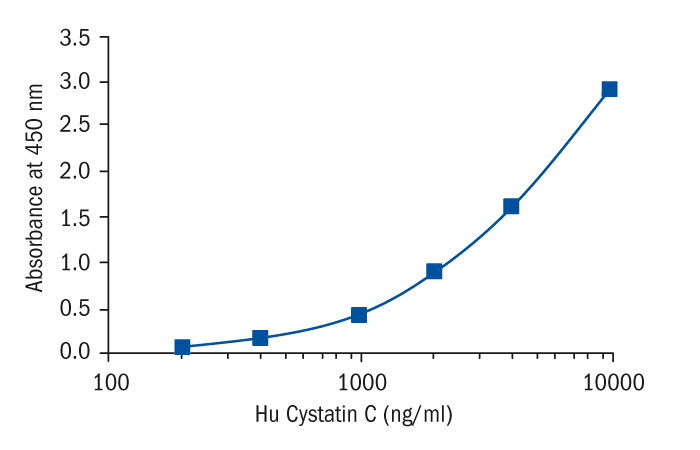
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
200–10 000 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.25 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 3.4 %
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 5; CV = 6.9 %
Spiking Recovery
95.0 %
Dilution Linearity
97.8 %
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-detectable
- dog Non-detectable
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- mouse Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
- monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:400)
Note
The kits are CE-IVD certified and intended for professional use.
Features
- European Union: for in vitro diagnostic use
- Rest of the world: for research use only!
- The total assay time is less than 2 hours
- The kit measures total cystatin C in serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin), urine and cerebrospinal fluid
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Quality Controls are human serum or human urine native protein based. No animal sera are used
- Standard is purified native protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use or concentrated
- Convenient for automatization
Research topic
Neural tissue markers, Renal disease
Summary
Cysteine proteinase inhibitors, cystatins superfamily, have been identified in animals, plants
and protozoa. All cystatins inactivate lysosomal cysteine proteinases, e.g. cathepsin B, H, K, L
and S as well as some structurally related plant proteinases, such as papain and actinidin.
Human cystatin C is produced at a constant rate by all nucleated body cells and occurs in all
body fluids abundantly. It is a non-glycosilated basic single-chain protein consisting of 120
amino acids with a molecular weight of 13.36 kDa and is characterized by two disulfide bonds
in the carboxy-terminal region. The protein is encoded by the CS73 gene located on the short
arm of chromosome 20.
Biological function of human cystatin C, and its role in various pathological states, has been the
subject of numerous studies. Imbalance between cystatin C and cysteine proteinases is
associated with diseases such as inflammation, renal failure, cancer, Alzheimer disease,
multiple sclerosis and hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy. Its increased level has been
found in patients with autoimune diseases, with colorectal tumors and metastases, patients
with inflammation and in patients on dialysis. Serum cystatin C concentration correlates
negatively with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) as well as or better than creatinine, therefore
was recently proposed as a new, very sensitive, marker of changes in GFR.
On the other hand, low levels of cystatin C come along the breakdown of the elastic laminae
and, subsequently, the atherosclerosis and abdominal aortic aneurysm, as indicate latest
publications. Results make evident association of cystatin C levels with the incidence of
myocardial infarction, coronary death and angina pectoris. Furthermore, cystatin C correlates
with triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, BMI and age of individuals. Thus, low concentration of
cystatin C presents a risk factor for secondary cardiovascular events.