Features
- European Union: for in vitro diagnostic use
- Rest of the world: for research use only!
- The total assay time is less than 5 hours
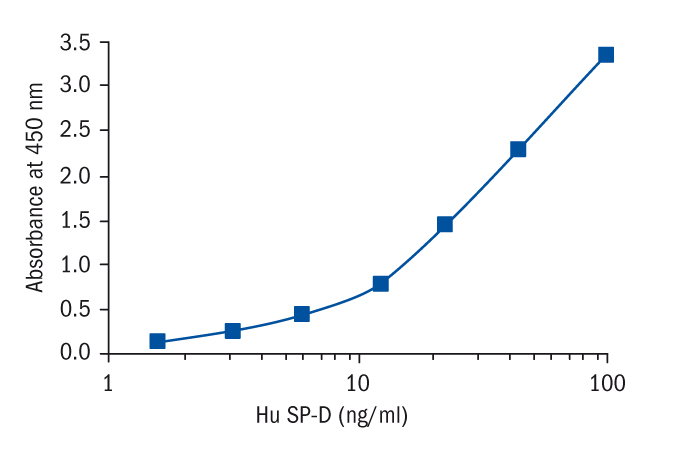
- The kit measures total surfactant protein D in serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin), bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and amniotic fluid
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Quality Controls are human serum based. No animal sera are used
- Standard is recombinant protein based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized
Research topic
Immune Response, Infection and Inflammation, Pulmonary diseases, COVID-19
Summary
Human Surfactant Protein D (SP-D) is a member of the collageneous subfamily of
glycoproteins and calcium-dependent lectins (collectins).
SP-D is a homotrimeric protein consisting of three 43kDa units that are bonded at their Ntermini.
Most preparations of SP-D contain predominantly dodecamers (four trimeric subunits),
but also higher multimers have been observed. Each unit consists of at least four discrete
structural domains: a short N-terminal domain; a relatively long collagenous domain, a short
amphipathic connecting peptide, and a C-terminal, C- type lectin carbohydrate recognition
domain (CRD).
SP-D is synthesized and secreted by two types of non-ciliated epithelial cells in the peripheral
airway, alveolar type II cells and Clara cells. It is also expressed by various epithelial cells in
the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts and placenta.
In the lungs, SP-D participates in the innate response to inhaled microorganisms and organic
antigens. SP-D acts by aggregating bacteria and viruses, leukocyte function and stimulating an
allergenic response. SP-D binds to the surface glycoconjugates of various microorganisms (eg,
influenza virus, HIV, HSV, RSV, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) and the oligosaccharides
associated with the surface of numerous organic antigens and enhances their phagocytosis.
Studies have shown that SP-D binds to T cells, thus inhibiting their proliferation. SP-D also
binds with inflammatory ligands via protein-protein and protein-carbohydrate interactions that
are effective in reducing specific inflammation. In addition, SP-D binds to apoptotic cells and
stimulates their phagocytosis by macrophages governed by mechanisms dependent and CD91
calreticulin.
Given that SP-D together with SP-A affects the reactivity of immune cells, their presence in the
endometrium and placenta plays an important role in protection against bacteria and toxins
during pregnancy. Reduced levels of all components of pulmonary surfactant, including SP-D,
has been linked to premature birth.
Disturbance of pulmonary surfactant is in many cases the reason for collapse of the lungs and
is also associated with many pulmonary diseases. All types of chronic lung disease is
characterized by pathologically altered levels in lung tissue (fibrosis and emphysema). Studies
have shown that expression of SP-D is associated with many pulmonary diseases: cystic
fibrosis, acute interstitial pneumonia (ARDS), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma,
bronchopulmonary dysplasia, alveolar capillary dysplasia, alveolar proteinase and tuberculosis.
Clinical application and areas of investigation: Cystic fibrosis, Acute interstitial pneumonia (ARDS), Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Asthma, Bronchopulmonary dysplasia, Alveolar capillary dysplasia and alveolar proteinase, Immune response, infection and inflammation