Human PCSK9 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) ELISA
Excellent biomarker for long term therapy.
Biomarker of cardiovascular risk and atherosclerotic process.
Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a well-established risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). The recent guidelines on lipid management emphasize treatment of individuals at increased risk for developing CVD events with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins) at doses proven to reduce CVD events. However, there are limited options for patients who are either intolerant to statin therapy, develop CVD despite being on maximally tolerated statin therapy, or have severe hypercholesterolemia.
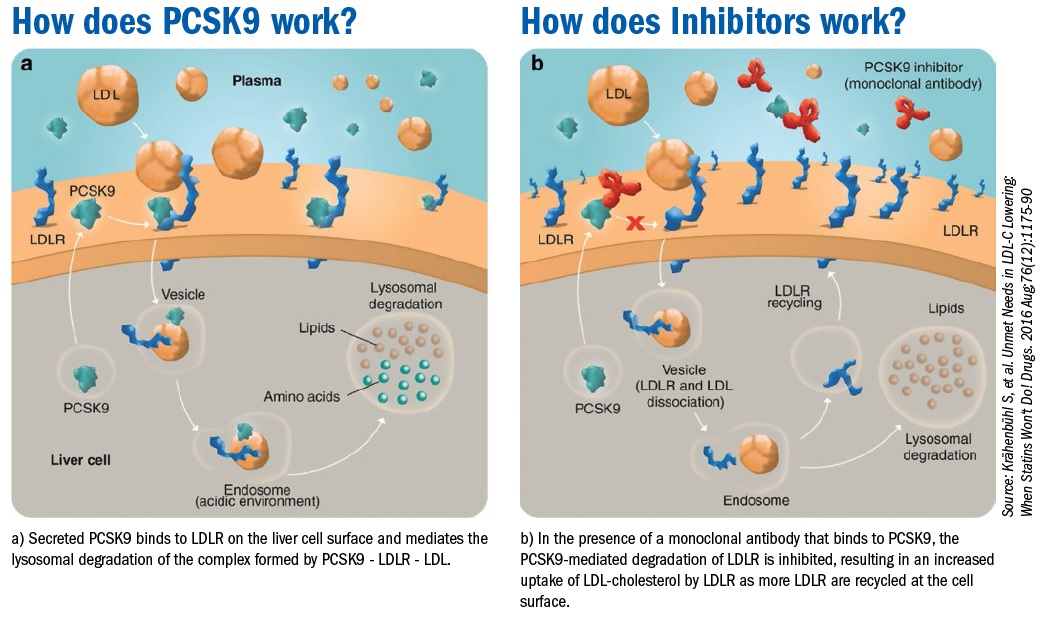
Recently the Food and Drug Administration approved two novel medications for low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol reduction: Evolocumab and Alirocumab. These monoclonal antibodies target and inactivate proprotein convertase subtilsin-kexin type 9 (PCSK9), a hepatic protease that attaches and internalizes LDL receptors into lysosomes hence promoting their destruction. By preventing LDL receptor destruction, LDL-C levels can be lowered 50%-60% above that achieved by statin therapy alone.
Positive outcomes of two important clinical trials, FOURIER (NCT01764633) and ODYSSEY Outcomes (NCT01663402) reviewing efficacy and safety of Evolocumab and Alirocumab, respectively, were published very recently.
European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society Task Force published their positive consensus statement on and practical guideline for the use of PCSK9 inhibitors in patients at very high cardiovascular risk in 2017.
PCSK9. What is it?
PCSK9 is a protein which is critically important in regulating low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels by significantly increasing the clearance of LDL-C by the liver.
Impact of PCSK9 inhibitors treatment:
↓ LDL cholesterol (50-60%)
↓ triglycerides (8-20%)
↓ total cholesterol (25-40%)
↑ HDL cholesterol (5-9%)
References
Krähenbühl S, et al. Unmet Needs in LDL-C Lowering: When Statins Won't Do! Drugs. 2016 Aug;76(12):1175-90.
Giugliano RP, et al.; FOURIER Investigators. Clinical efficacy and safety of achieving very low LDL-cholesterol concentrations with the PCSK9 inhibitor evolocumab: a prespecified secondary analysis of the FOURIER trial. Lancet. 2017 Oct 28;390(10106):1962-1971.
Bohula EA, et al. Inflammatory and Cholesterol Risk in the FOURIER Trial. Circulation. 2018 Jul 10;138(2):131-140.
Schwartz GG, et al. Effect of alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, on long-term cardiovascular outcomes following acute coronary syndromes: rationale and design of the ODYSSEY outcomes trial. Am Heart J. 2014 Nov;168(5):682-9.
Landmesser U, et al.; European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society Task Force consensus statement on proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors: practical guidance for use in patients at very high cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2017 Aug 1;38(29):2245-2255.
