Update 2026: miREIA assay kits have been discontinued as of January 1, 2026.
The microRNA project now continues exclusively on the Two-Tailed RT-qPCR (TT-PCR) platform.
Small interfering microRNA molecules (miRNAs) are non-coding RNA regulatory molecules that control a wide array of biological processes by translational inhibition. Due to their ability to be released into the blood as well as their sufficient stability in body fluids, miRNAs are used as specific biomarkers of numerous physiological and pathophysiological cellular processes.
Coronary artery disease is the most prevalent cause of mortality worldwide. The most sudden manifestation is acute myocardial infarction. Presently, in addition to electrocardiogram evaluation, diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction relies on the assessment of blood-based sensitive and specific biomarkers such as cardiac troponins. The search for other specific and sensitive biomarkers is still ongoing as some false positive and false negative results based on troponin remain. The miRNAs are promising candidates as they exhibit tissue-specific expression patterns during healthy states, but also changes during development and establishment of diseases.
For diagnosis purposes, increase or decrease of specific miRNAs can be monitored from plasma or serum samples by different molecular techniques, mostly based on PCR. Additionally, there are newly emerging quantitative ELISA-like methods based on immunoassay technology.
myomiRs Network
The recently described muscle-specific miRNA (myomiR) network has a central role in the regulation of skeletal muscle plasticity by coordinating changes in fiber type and muscle mass in response to altered the miRNAs most abundant in the skeletal or heart muscle. The myoMIR network includes hsa-miR-1, hsa-miR-133, hsa-miR-208, and hsa-miR-499, and are among the most intensively characterized miRNAs in investigations of cardiac pathologies. These miRNAs have increased expression in plasma or serum samples from patients with acute myocardial infarction. The hsa-miR-208 expression pattern after acute myocardial infarction is similar to the cardiac specific troponin.
Some other miRNAs, like the hsa-miR-499-5p, allow discriminating between patients with non-ST elevated myocardial infarction, patients with acute heart failure without acute myocardial infarction and controls.
The other miRNAs, hsa-miR-122, hsa-miR-133a, hsa-miR-134, hsa-miR-145, and hsa-miR-370 have been associated with coronary artery disease.
Differentiating between forms of heart disease
A question remains whether miRNAs might be able to discriminate between patients with stable angina pectoris and those with acute myocardial infarction. Some potential candidates exist, i.e. hsa-miR-1, hsa-miR-133a, and hsa-miR-208b.
Several miRNAs have been reported which are able to discriminate between the different forms of cardiac disease. The hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-25, hsa-miR-92, hsa-miR-106b, hsa-miR-126, and hsa-miR-451 are significantly elevated in unstable angina compared with stable angina pectoris and healthy controls.
Also, hsa-miR-186, hsa-miR-132 and hsa-miR-150 are differentially expressed in patients with unstable angina, patients with chest pain of non-cardiac origin and healthy controls.
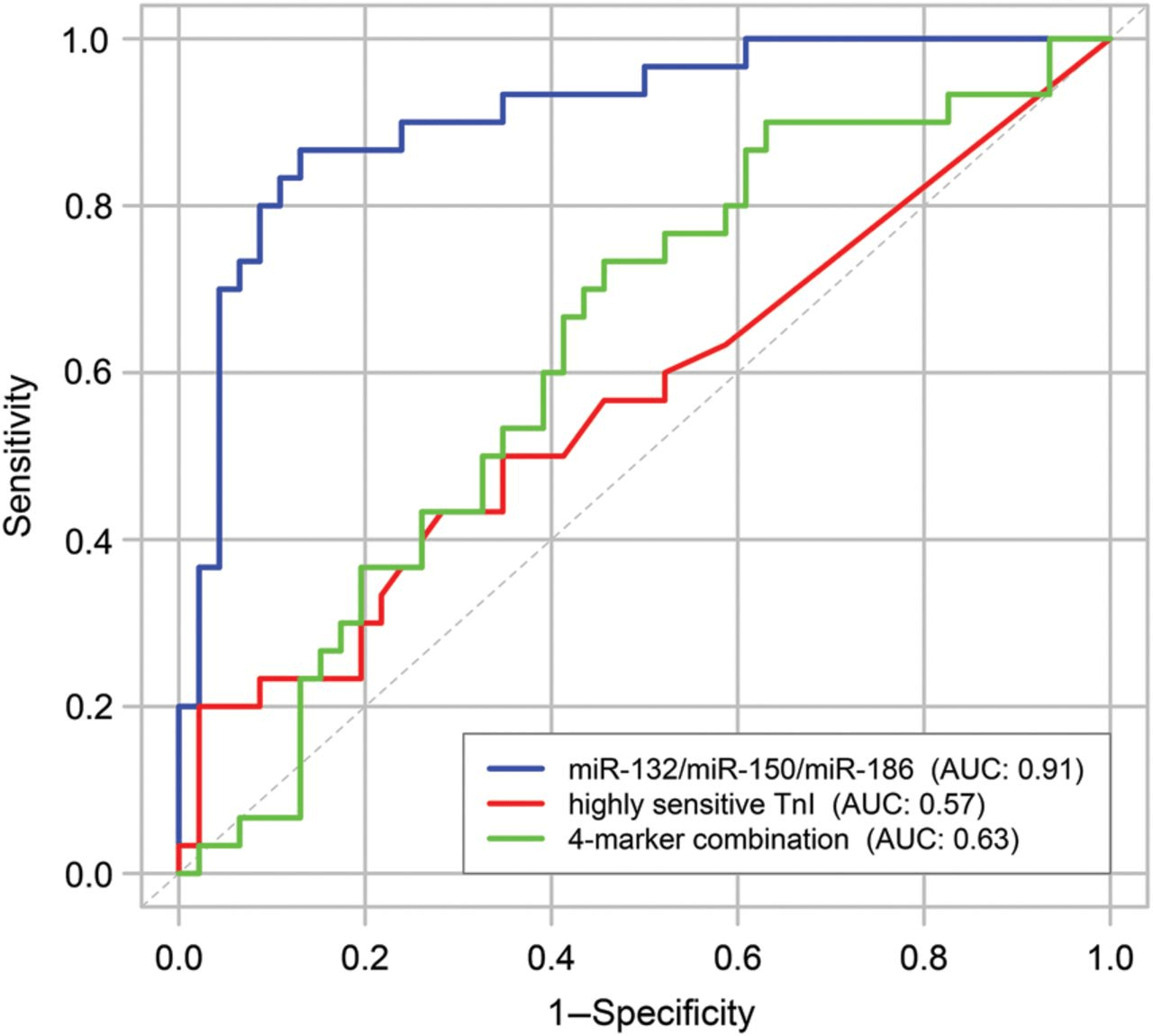
The illustration shows receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves and area under the ROC curve (AUC) are given for the 3-miRNA panel (miR-132, miR-150, and miR-186) compared with troponin I measured by a high-sensitivity assay (hsTnI) and a model including hsTnI, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), C-reactive protein, and Cystatin C (4-marker combination).
miRNAs as predictor for future personal risk status
MiRNAs can also be used as predictors for future personal risk status. A diagnostics panel has been postulated by Bye et al., which includes hsa-miR-106a-5p, hsa-miR-424-5p, hsa-let-7g-5p, hsa-miR-144-3p, and miR-660-p. These five miRNAs improved the predictive power of Framingham Risk Score, i.e. increased the area under the curve from 0,72 to 0,91.
Another research group published a tool for discrimination between healthy subjects and patients with coronary artery disease based on expression levels of hsa-miR-150-5p, hsa-miR-101-3p, hsa-miR-141-3p, and hsa-miR-200b-3p.
Vision of the future
Current reports provide a large number of miRNAs as possible candidates of CAD related diseases. However, most human studies used diverse preparation protocols and rather small sample sizes. In addition, medication use was not always sufficiently accounted for.
At the moment, it is clear that further studies have to be conducted in larger and more homogeneous study populations, with greater adherence to universally used and therefore comparable preparation methods.
In the future, however, it can be expected that miRNAs might emerge as biomarkers superior to well-established biomarkers exemplified by cardiac troponins.
Sources: Molecular Biology Reports, DOI: 10.1007/s11033-019-04963-9
JMCC, DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.05.009
European Heart Journal, DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu151
