Update 2026: miREIA assay kits have been discontinued as of January 1, 2026.
The microRNA project now continues exclusively on the Two-Tailed RT-qPCR (TT-PCR) platform.

Cardiovascular disease - a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among adults - is strongly influenced by platelet function through acute thrombotic and atherogenic mechanisms.
What causes an acute myocardial infarction?
The usual cause of sudden coronary occlusion is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus). The blood clot typically forms inside a coronary artery that already has been narrowed by atherosclerosis or "hardening of the arteries", a condition in which fatty, calcified plaques build up along the inside walls of blood vessels.
Pathways that regulate platelet activity and lead to coronary occlusion are central to the pathogenesis of acute coronary syndromes. Platelet activation contributes to other thrombotic disorders and cardiovascular diseases.
The platelets include microRNAs (miRNAs), which are small noncoding RNAs involved in many molecular processes, most notably regulation of gene expression.
In addition to their role in thrombosis, platelets might have an important role in maintaining vascular health (such as angiogenesis) and disease, including potentially contributing to the development of atherosclerotic plaque. Platelets also participate in cell-to-cell transfer of both mRNAs and miRNAs, providing a potential role for miRNAs as intercellular regulators of vascular homeostasis.
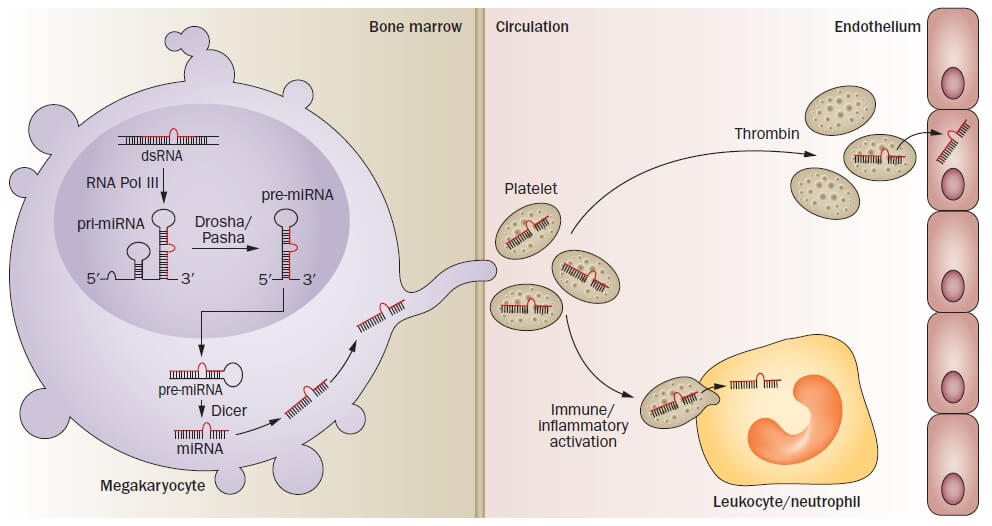
In addition, evidence suggests that platelet-derived miRNAs might have important roles as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease susceptibility, prognosis, or treatment.
Balancing the intensity and duration of antiplatelet therapy according to thrombotic risk is a fundamental need in order to optimize therapy effectiveness and safety. Incorporation of new predictors in thrombotic risk stratification is therefore of a crucial importance for antiplatelet therapy net clinical benefit.
Researchers involved in a genetic substudy of the Multicenter randomized trial PRAGUE-18.
have focused on miRNAs miR-126-3p and miR-223-3p, new markers of platelet activation, in order to facilitate predictions of recurrent thrombotic events after acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
This study involved 14 cardiac centers in the Czech Republic. The analysis included 598 patients randomized in the Prague18 study (ticagrelor vs. prasugrel in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The average age of patients was 62 years and males accounted for 77.8% of subjects.
How were miRNAs selected in this study?
- miR-126-3p and miR-223-3p are exclusively platelet/ megakaryocyte origin
- miR-126-3p is associated with platelet activation; miR-223-3p is related to aggregation/ granule secretion
- determination of the selected miRNA responds to main platelet activating signal via several pathways (VEGF signalling, VCAM-1, SPRED1 and PIK3R2/p85-beta, P2Y12 receptor, RPS6KB1/HIF1a), and corresponds to platelet-signal generated in-vivo
During the study follow up, 40.6% of patients switched to clopidogrel. Blood samples were collected 24 hours after admission.
Quantitative determination of selected miRNAs was performed with a novel microRNA immunoassay method using monoclonal antibodies to detect DNA/ miRNA hybrids and colorimetric visualization (miREIA, BioVendor).
Levels of miR-126-3p and miR-223-3p were normalized by miR-423-3p and miR-150-5p.
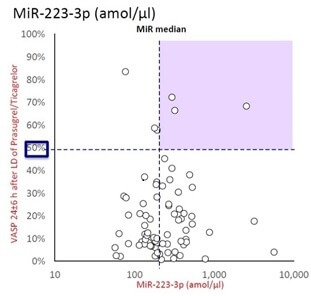
Selected miRNAs were compared with key efficacy endpoints and analysed using univariate and multivariate logistic regressions for adjustment of the miRNAs influence on endpoints for potential confounding factors.
- Ischemic endpoints: study arm, switch to clopidogrel, age, sex, BMI, cigarette smoking, history of hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, previous myocardial infarction (MI), CPI, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), chronic heart failure, chronic renal failure, peripheral arterial disease, left bundle branch block (LBBB), right bundle branch block (RBBB), time from symptom onset hospital, number of diseased vessels > 1, stem disease, thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) < 3 after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Bleeding endpoints: age, sex, switch to clopidogrel, chronic kidney dysfunction, hemoglobin, creatinine, history of bleeding and proton pump inhibitor therapy
Research data show that increased values of miR-223-3p were significantly related to the occurrence of combined ischemic endpoint within 30 days [OR (95% CI)] and within one year
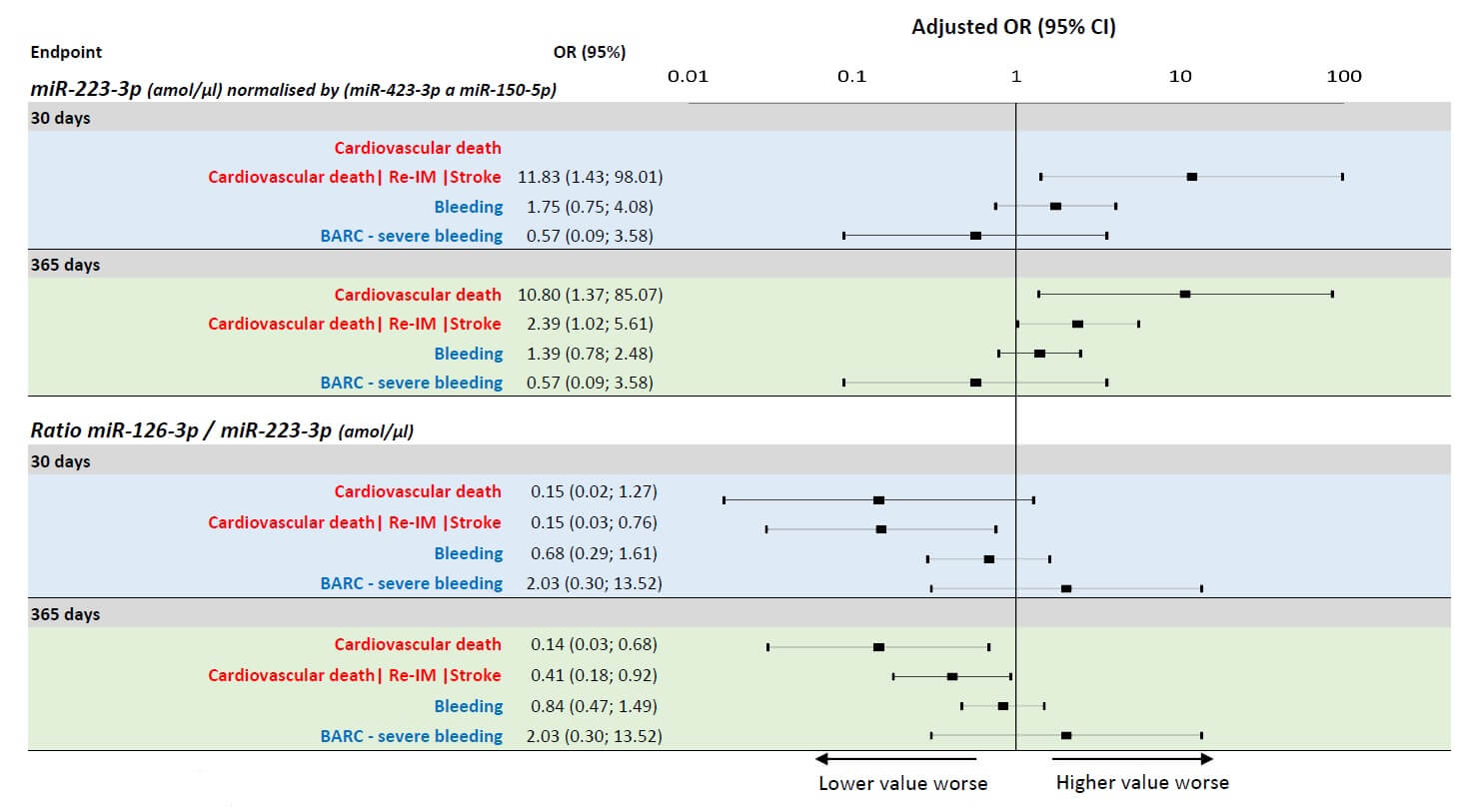
Scientists found that decreased ratio of miR-126-3p/miR-223-3p was significantly related to the occurrence of combined ischemic endpoint within 30 days and at one year.
MiRNAs were identified as independent predictors even after adjustment for confounding clinical predictors.
It was noteworthy that no association between miRNA and bleeding complications was identified.
To conclude..
Authors of this study revealed that the miR-223-3p and miR-126-3p to miR-223-3p ratio are strong independent predictors of short and long-term thrombotic events and can be used used as an additional biomarker for ischemic risk stratification of patients after AMI.
If this miRNA panel could be used in clinical diagnostic laboratories, it could be a revolutionary tool in the screening of AMI patients.
