
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a heterogeneous multivariate pregnancy disease with complicated pathological mechanisms. In addition to inflammatory reaction, insulin resistance (IR) and abnormality of lipid and glucose metabolism, GDM also involves DNA methylation and oxidative stress signal transduction that affect cardiac function.
Statistics show that the increase in the prevalence of GDM is global and 33.33% of GDM pregnant women will suffer from postpartum depression!
The difference between GDM and diabetes mellitus is sex specificity and temporality, while IR is a similar feature between GDM and diabetes mellitus. According to statistics, ~2-6% of total pregnancies in Europe involve GDM, and nearly half of GDM patients are highly likely to develop diabetes within 10 years.
The pathophysiological mechanism of GDM involves chronic low grade inflammation, insulin secretion deficiency and abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism caused by obesity.
Early diagnostic tools
We can explore new early diagnostic tools and potential therapeutic targets for GDM from three angles — improving chronic inflammatory response, increasing insulin sensitivity and maintaining glucose and lipid metabolism balance.

Chemerin is an inflammatory adipocyte factor and chemoattractant protein secreted by adipocytes. Studies have shown that high levels of Chemerin are associated with poor prognosis of preeclampsia, polycystic ovary syndrome, GDM and other pregnancy diseases. The higher the Chemerin level of GDM patients in early pregnancy, the greater the risk of GDM development. Thus it is suggested that Chemerin can be used as a predictive marker of GDM development risk.
FABP4 (a member of the fatty acid-binding protein [FABP] family, a group of small molecular proteins that act as fatty acid transporters in cells) can enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce atherosclerosis. It has already been found that FABP4 is overexpressed in GDM patients and has a significant positive correlation with IR and inflammatory factor TNF α, suggesting that FABP4 can be used as a new biomarker for GDM.
To cut a long story short: Chemerin and FABP4 are both inflammatory adipocyte factors expressed in adipocytes, both of which are related to the development and progression of GDM.
A research group from The People's Hospital of Zhangqiu Area (Jinan, China) have explored the diagnostic value and therapeutic potential of Chemerin and FABP4 in GDM patients by detecting the expression of Chemerin and FABP4 in peripheral blood samples.
Sixty patients with GDM, age 20-35 years,admitted from March 2018 to March 2019 were selected as the study group and another 50 healthy pregnant women corresponding in age and pregnancy were selected as the control group.
Inclusion criteria of this study:
Patients who met the standards formulated by the American Diabetes Association in 2012. After 75 g glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks of gestation, GDM was diagnosed if any one of following was present: fasting blood glucose over 5.1 mmol/l, blood glucose over 10.0 mmol/l for 1 h, blood glucose over 8.5 mmol/l for 2 h.
Exclusion criteria:
Patients with communication barrier or severe mental disorder; patients comorbid with malignant tumor or serious cardiac, lung, liver, kidney and other dysfunction; pregnant women with hypertension or endocrine and metabolic diseases before pregnancy.
Elbow venous blood (5 ml) was extracted from subjects on an empty stomach in the morning. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the expression of Chemerin, FABP4, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum.
Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the correlation between chemerin, FABP4 and inflammatory factors IL‑6, TNF‑α. The results showed that chemerin and FABP4 were positively correlated with inflammatory factors IL‑6 and TNF‑α (r=0.658, P<0.001; r=0.672, P<0.001; r=0.648, P<0.001; r=0.649, P<0.001).
In addition, the expression of Chemerin and FABP4 in the control group were significantly lower than that in the study group.
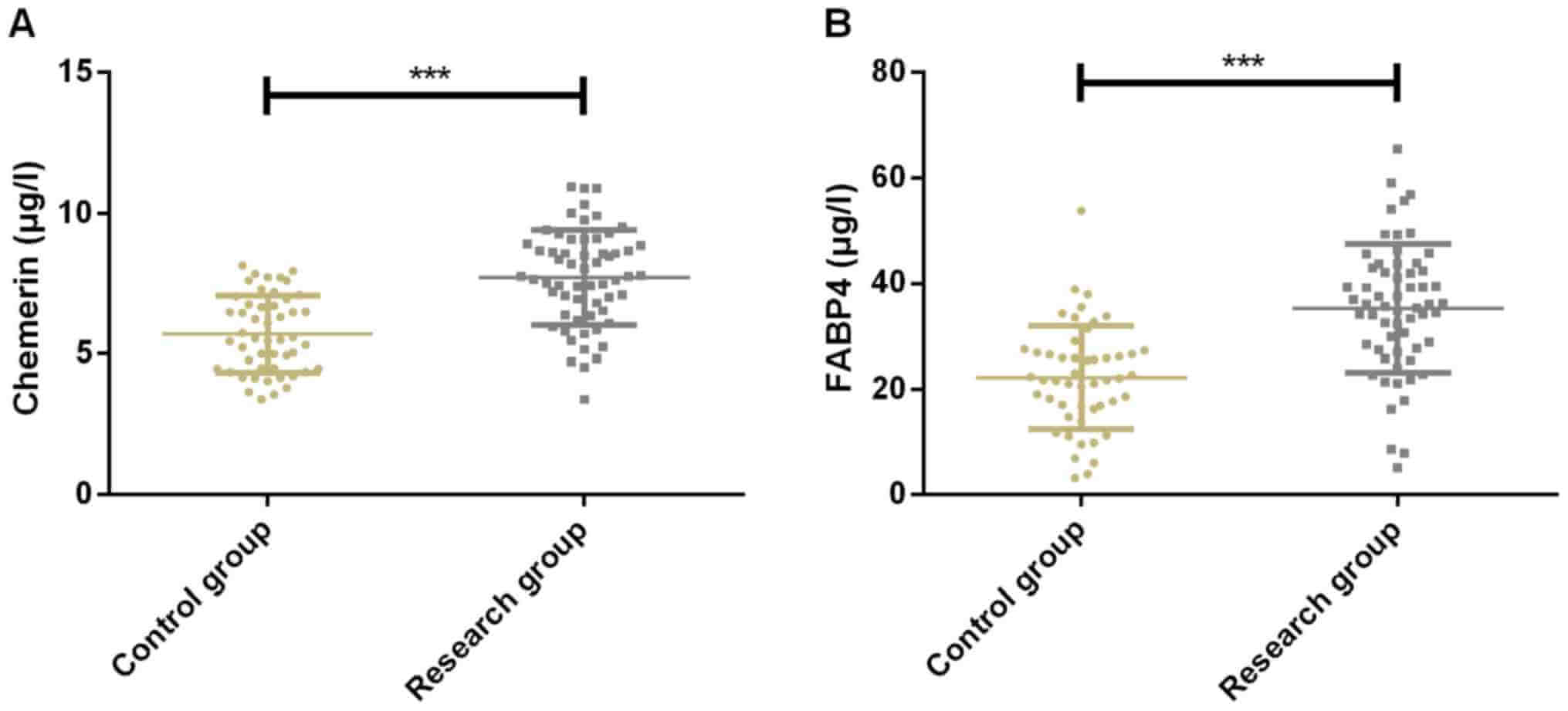
Expression of inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α of patients in the control group was significantly lower than that in the study group (P<0.001).
This study confirmed the positive correlation between Chemerin and FABP4, both of which are overexpressed in Gestational diabetes mellitus patients and have positive correlation with inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α.
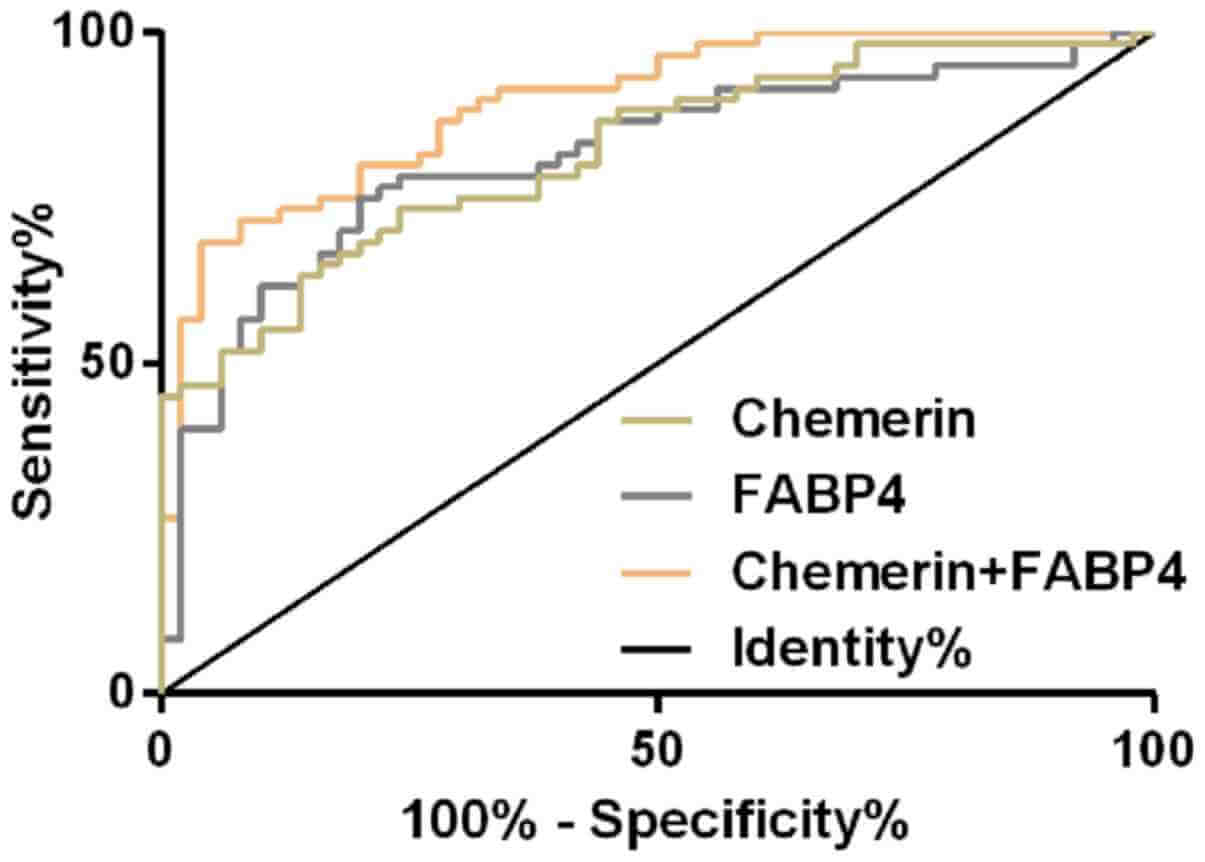
Research data also show that Chemerin and FABP4 have satisfactory diagnostic value for Gestational diabetes mellitus patients and inhibition of chemerin and FABP4 expression can be used as potential therapeutic targets for GDM patients.
Sources: Exp Ther Med, DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8247
